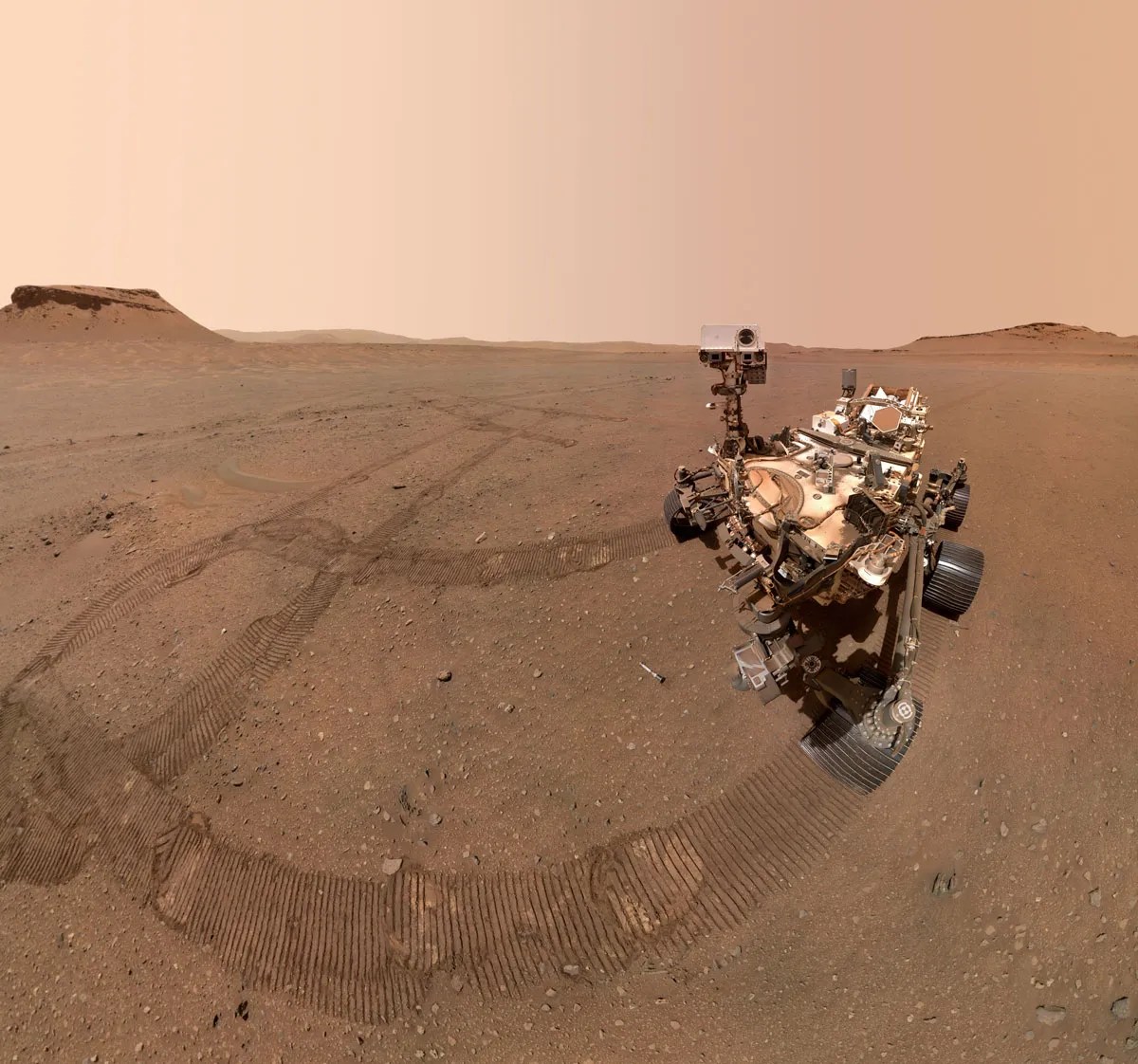
3 min read

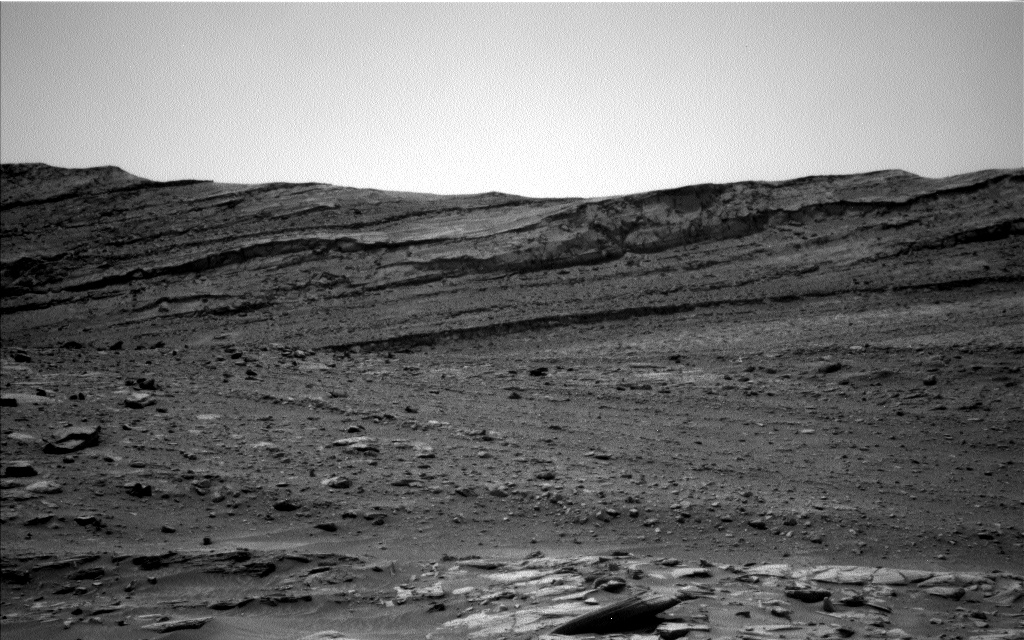
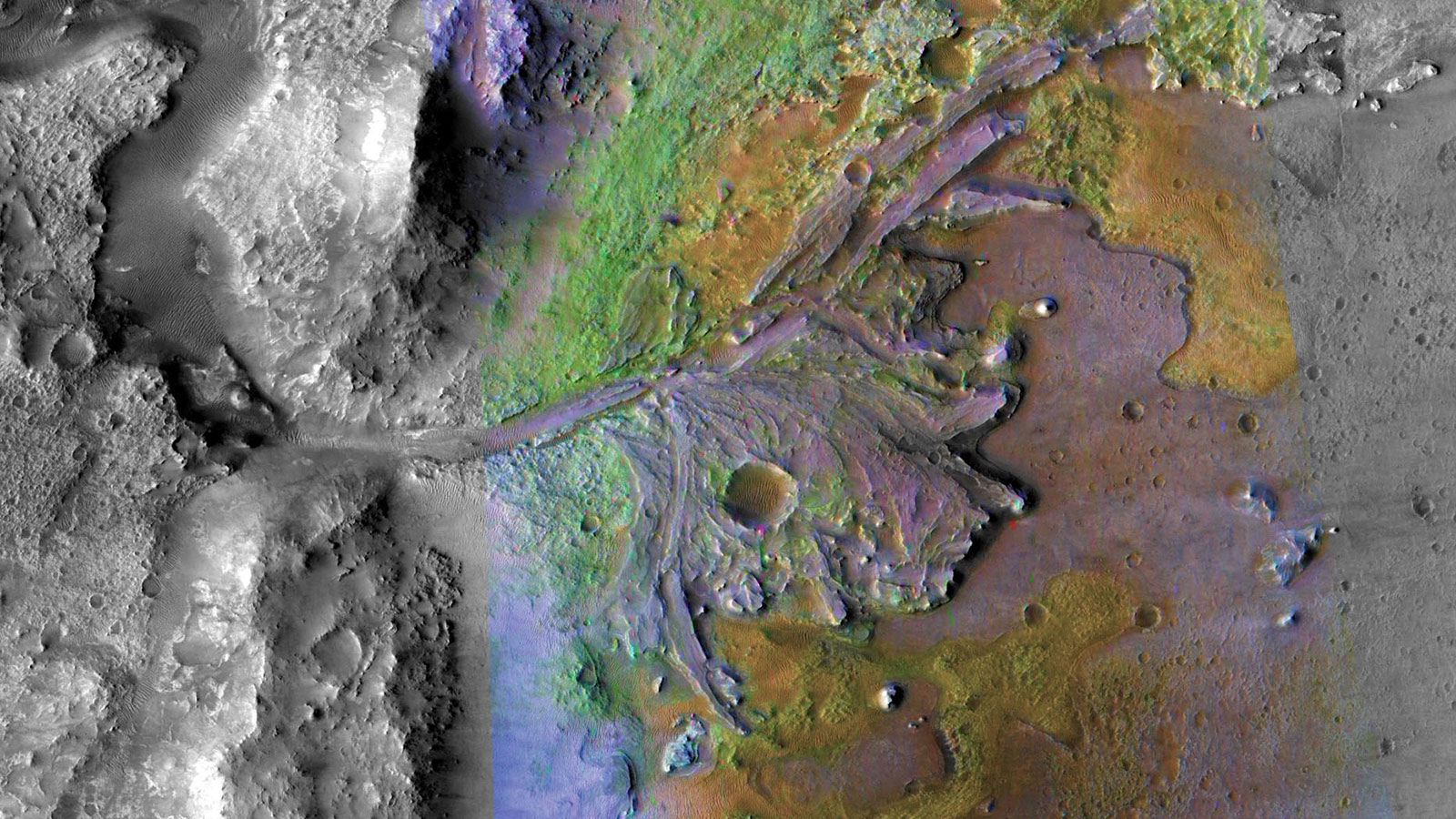
One of the prime objectives of the Perseverance mission is to collect a diverse cache of rock samples for eventual return to Earth. Among the highest priority rocks to sample are those that make up the well-preserved delta located on the western side of Jezero crater. This delta was one of the key attributes that made this landing site so appealing for the search for ancient Martian life. Close examination of deltaic rocks is critical for interpreting their depositional environment and establishing whether this paleoenvironment may have been habitable.

Since landing in Jezero crater last year, the rover has been investigating and drilling crater floor rocks to add to the sample cache. But the rover hadn’t yet had access to the coveted deltaic rocks—until now, that is. After conducting a “rapid traverse”
, Perseverance finally arrived at the delta front. Last week the rover parked at a site called Enchanted Lake, where the team was hopeful we might sample deltaic rocks for the very first time. But the rover can only collect a finite number of samples so the team has to carefully weigh all options, keeping in mind what has already been sampled and also trying to anticipate what we might encounter along the rest of the traverse. Even though we’re eager to drill into the delta, we have to be judicious.
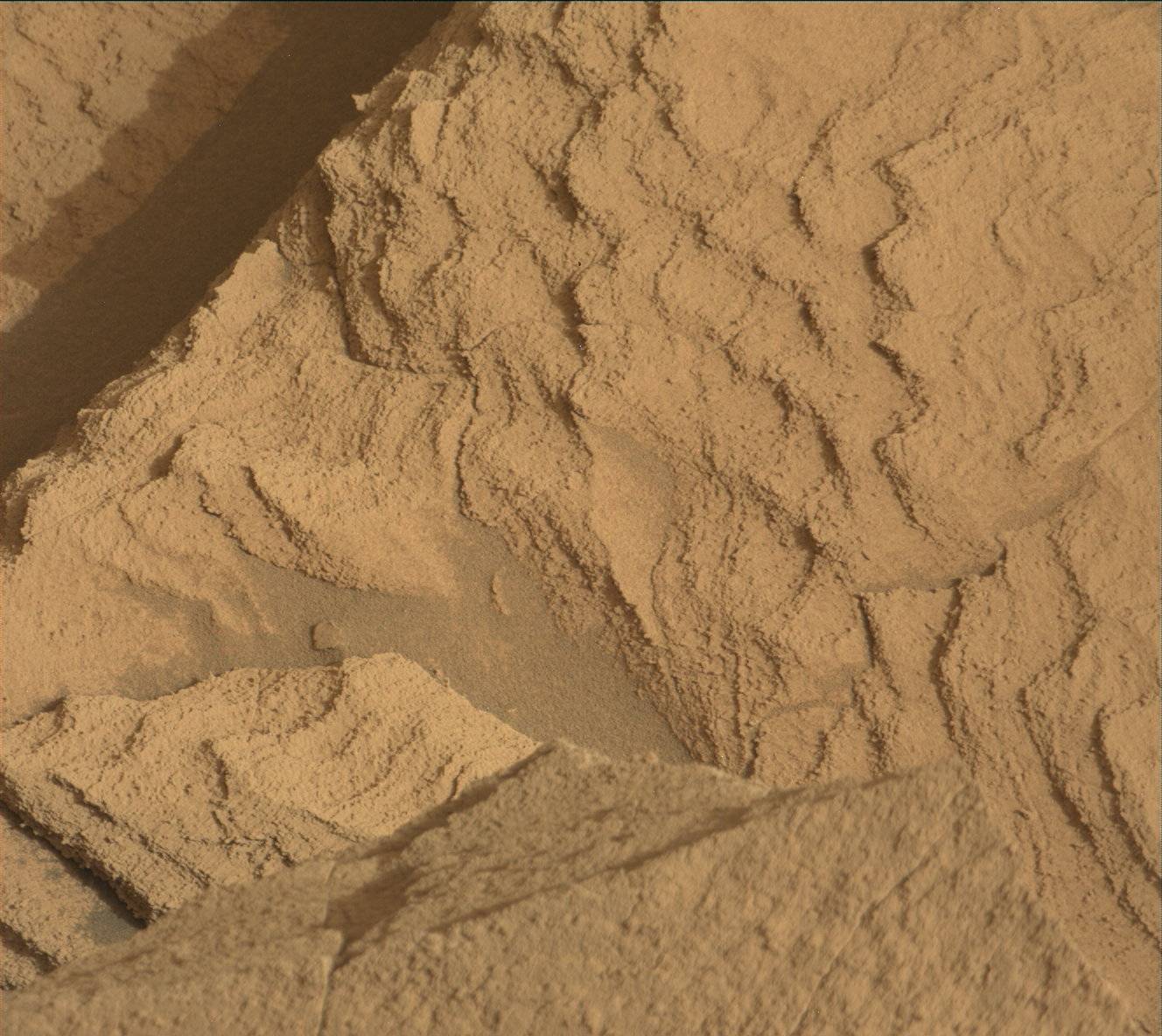
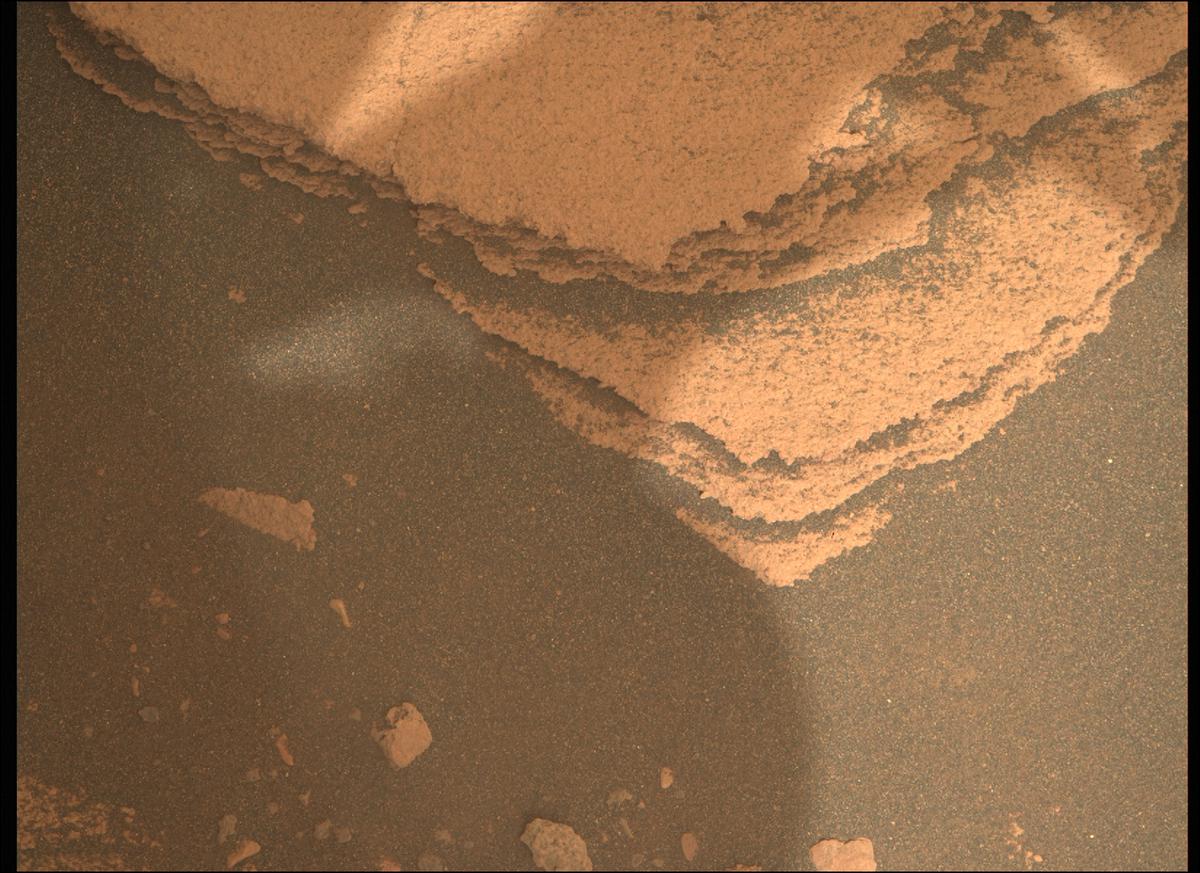
So, our first action item at Enchanted Lake was to examine the rocks there using the rover’s remote science instruments in order to decide whether they fit the desired criteria for sampling. The rocks at this site displayed many distinct—and interesting!—characteristics compared to the others we have studied thus far in Jezero. Yet after a thorough assessment, the team decided to forego sampling at this location. It was a tough decision to make, but we feel optimistic about the opportunities that lie ahead. The data collected at Enchanted Lake will be used instead to build context for future investigations of the delta.
The rover is now headed east toward a location called Hawksbill Gap, another promising location for sampling the delta. While traversing along the delta front, Perseverance will continue to collect data to help characterize the contact between the crater floor and deltaic rocks before ascending onto the delta itself. But our long-awaited sample of delta rocks? For that, we’ll have to wait just a little bit longer.
Written by Mariah Baker, Planetary Scientist at Smithsonian National Air & Space Museum