2 min read
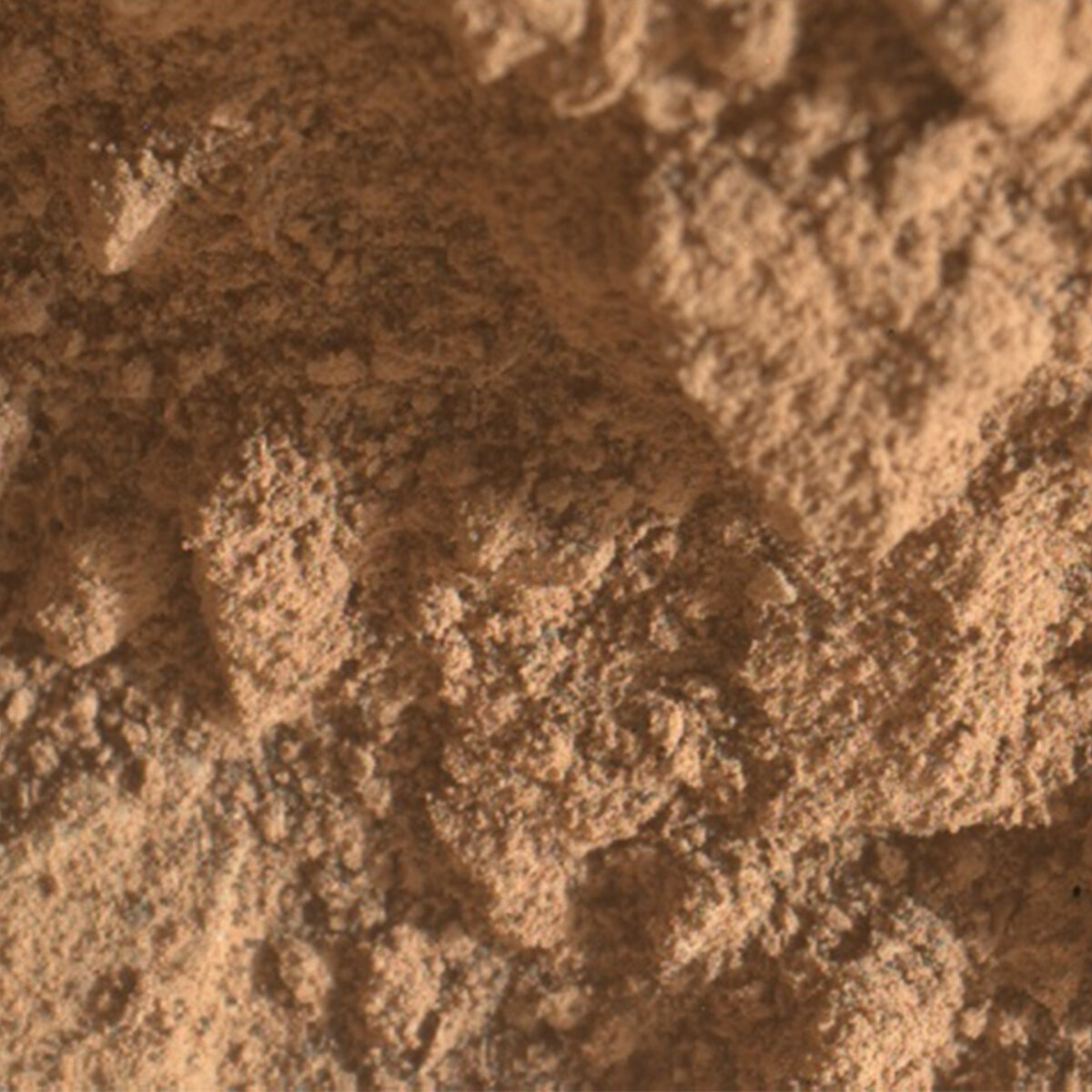

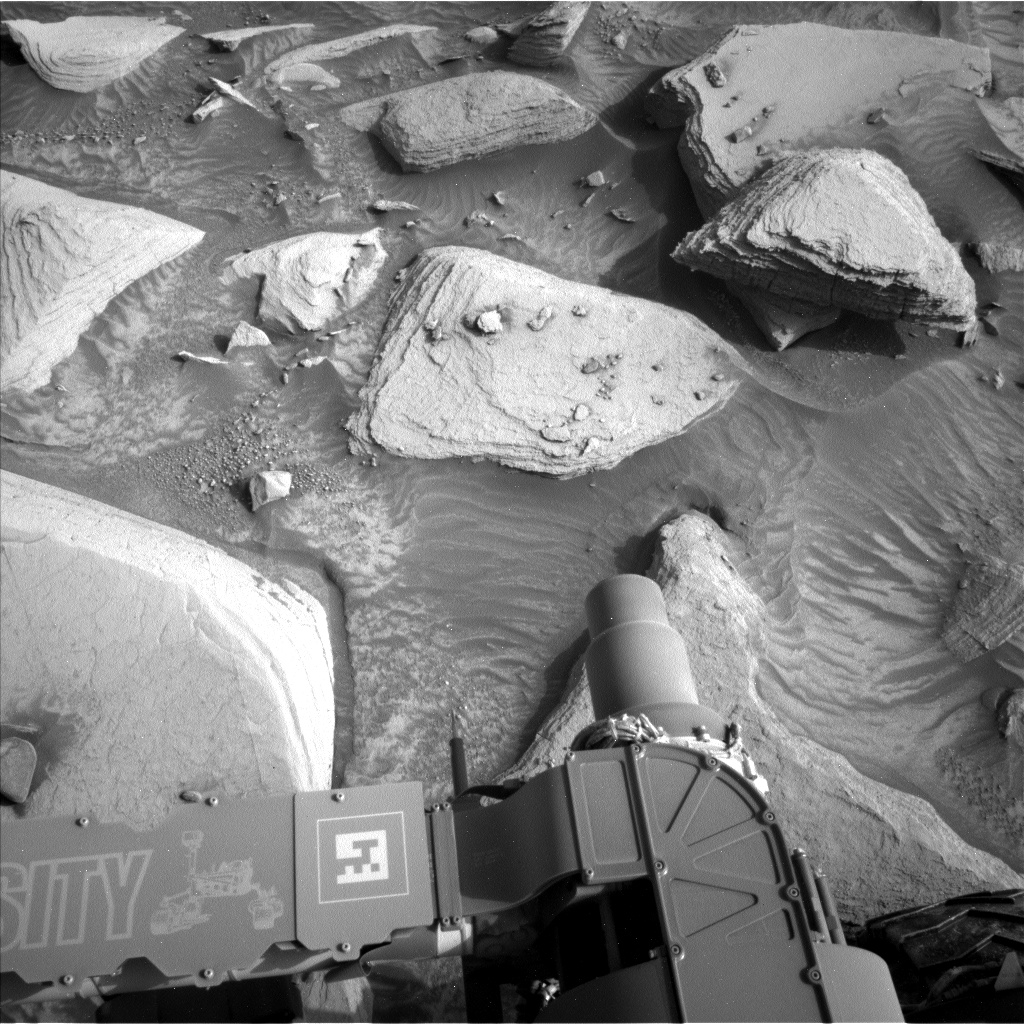
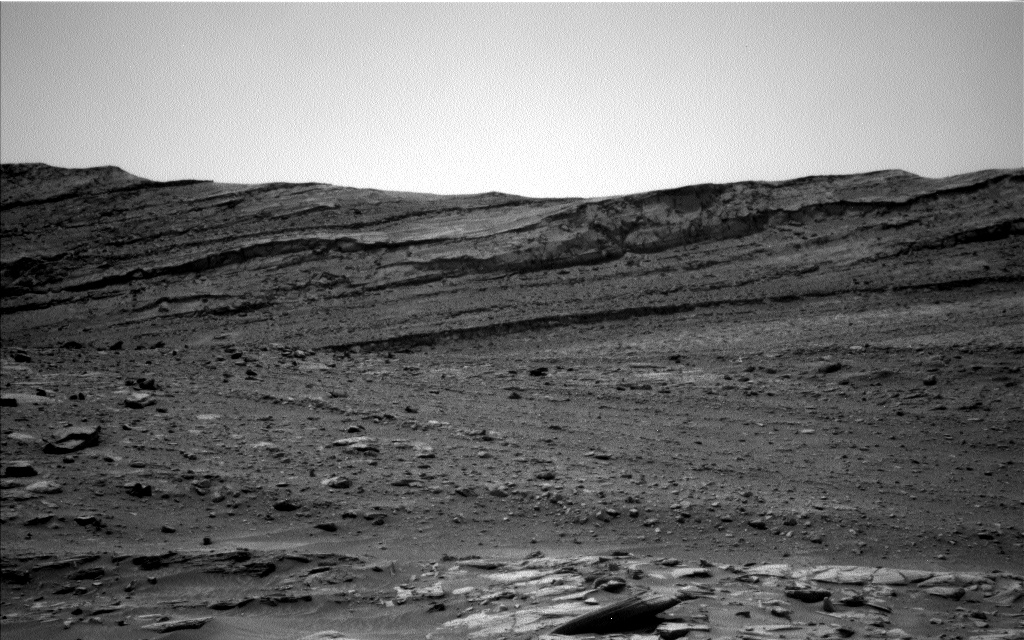
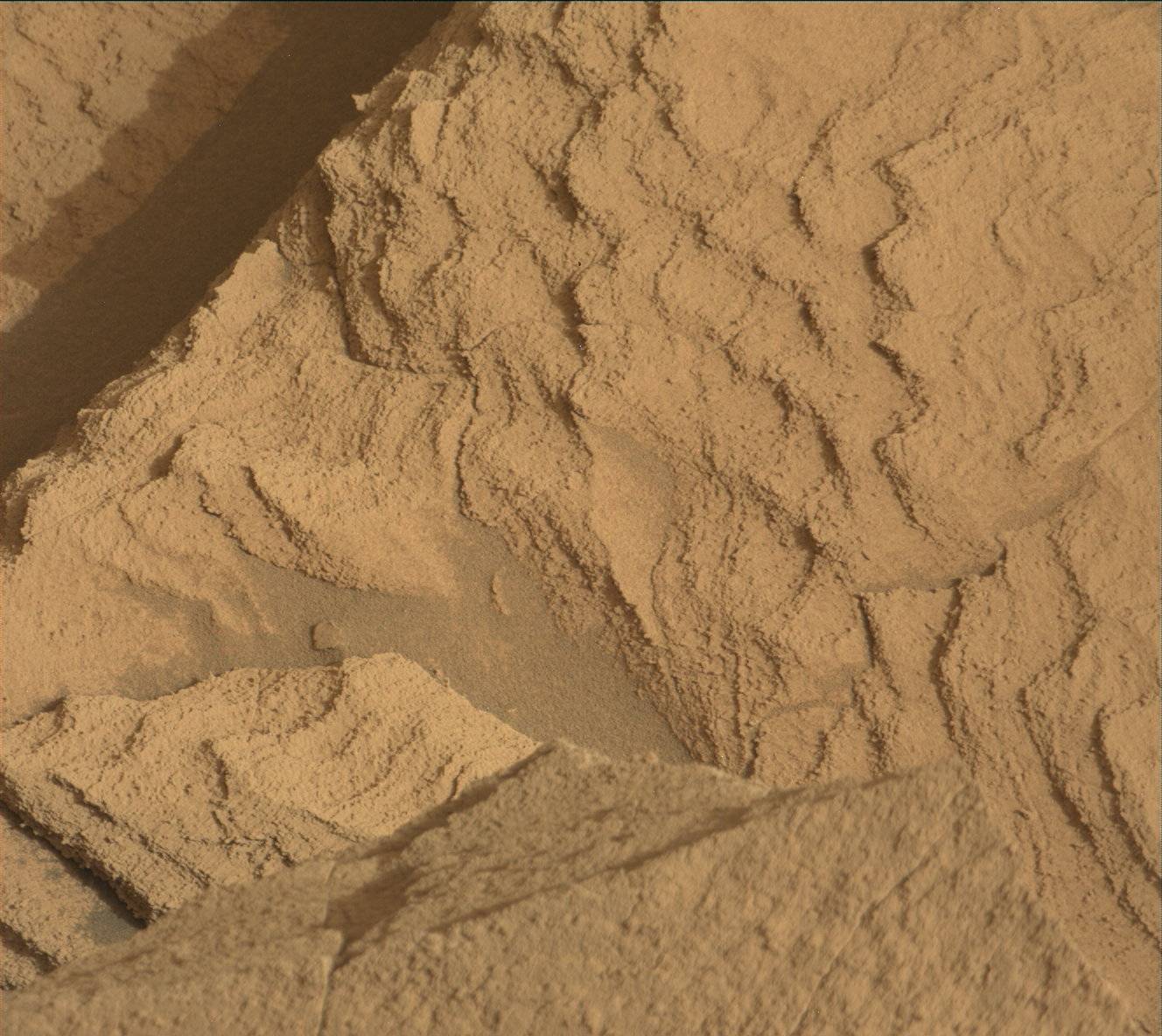
The MAHLI images acquired on Sol 3528 confirm that the APXS was well placed over the Avanavero drill tailings, and the APXS data look good so we are ready to drive away from this location. But first, we are planning a few more MAHLI and remote sensing observations. ChemCam will shoot its laser at a vein target named "Chiung" on the right side of the rover, then will acquire another RMI mosaic to extend the coverage of a bright mound with numerous veins. Mastcam will also extend stereo coverage of the "Amacuro" outcrop, document ChemCam's Chiung target, and monitor changes in the distribution of material on the rover deck. After Navcam searches for dust devils, Mastcam will look for changes in nearby rover tracks at Kamana. The arm will then be deployed to acquire another MAHLI image of the drill tailings to determine whether the APXS touched the tailings during the overnight integration planned on Sol 3528. MAHLI will also take images from 25 and 5 cm of a vein named "La Laja." Then the arm will be stowed for the drive. We are not expecting to receive as much data as usual for future planning, so downlink priorities were carefully reviewed, especially for the post-drive images.
Written by Ken Herkenhoff, Planetary Geologist at USGS Astrogeology Science Center