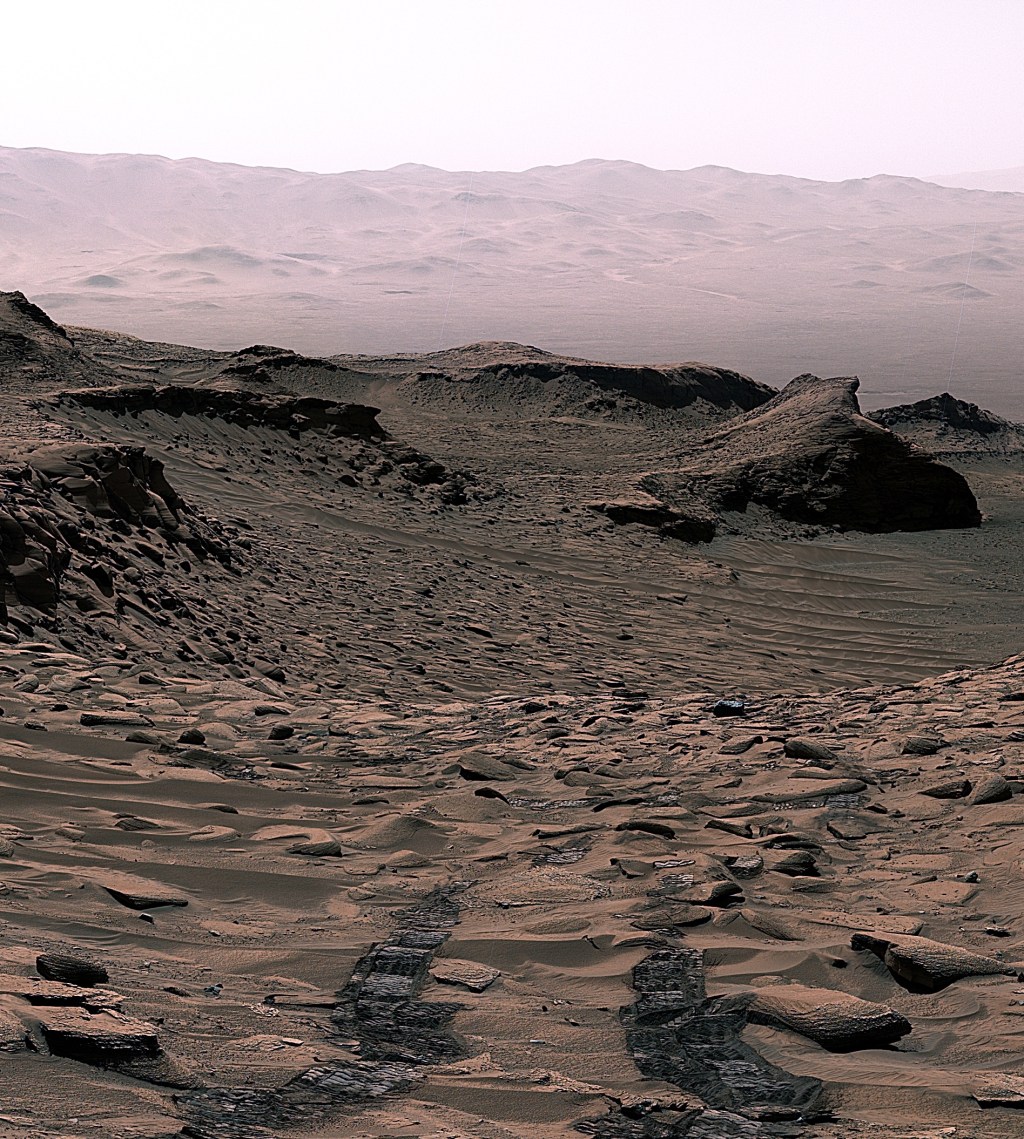
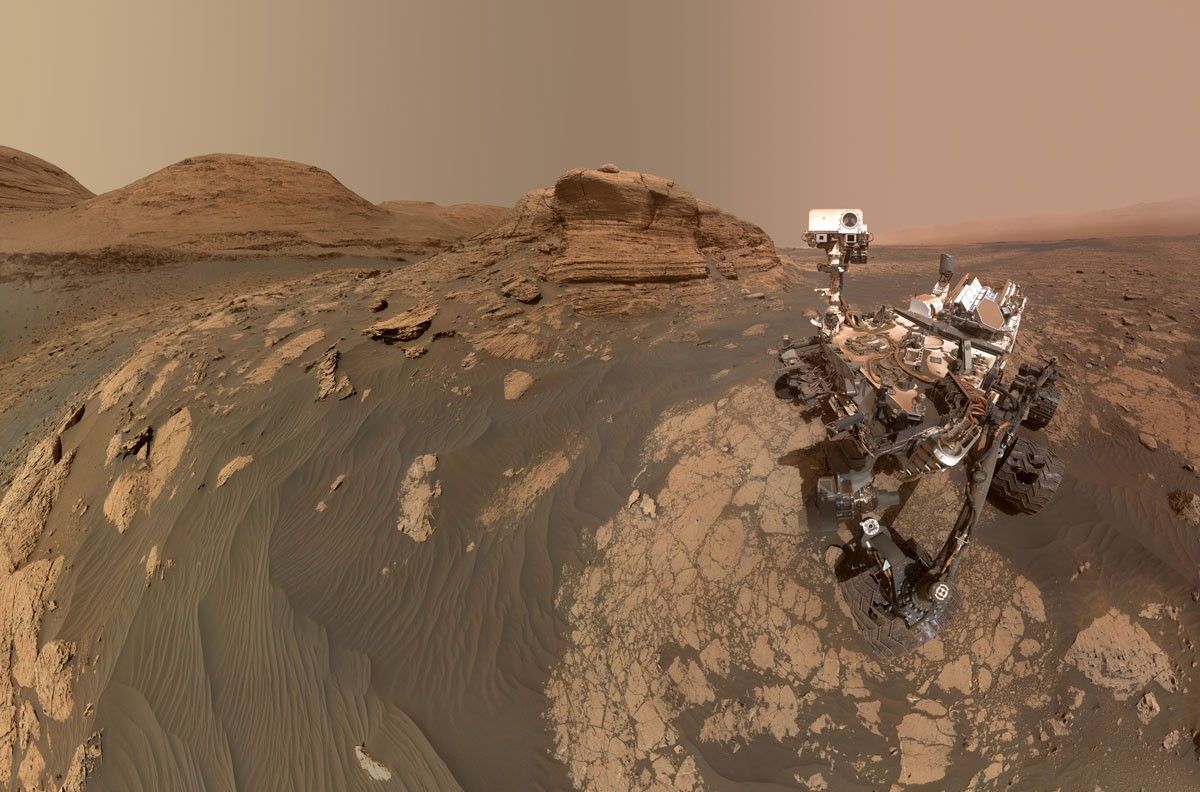
Curiosity is currently trekking east along a small detour due to recent challenges on steep, rocky, sandy terrain.
Earth planning date: Tuesday, June 20, 2023
Curiosity is currently trekking east along a small detour due to recent challenges on steep, rocky, sandy terrain. Today we planned 1 sol known as a ‘Touch and Go’: Curiosity spends a short time collecting science data including contact science activities, and then drives away on the same sol. These are useful plans when you have places to be, but don’t want to miss out on anything along the way!
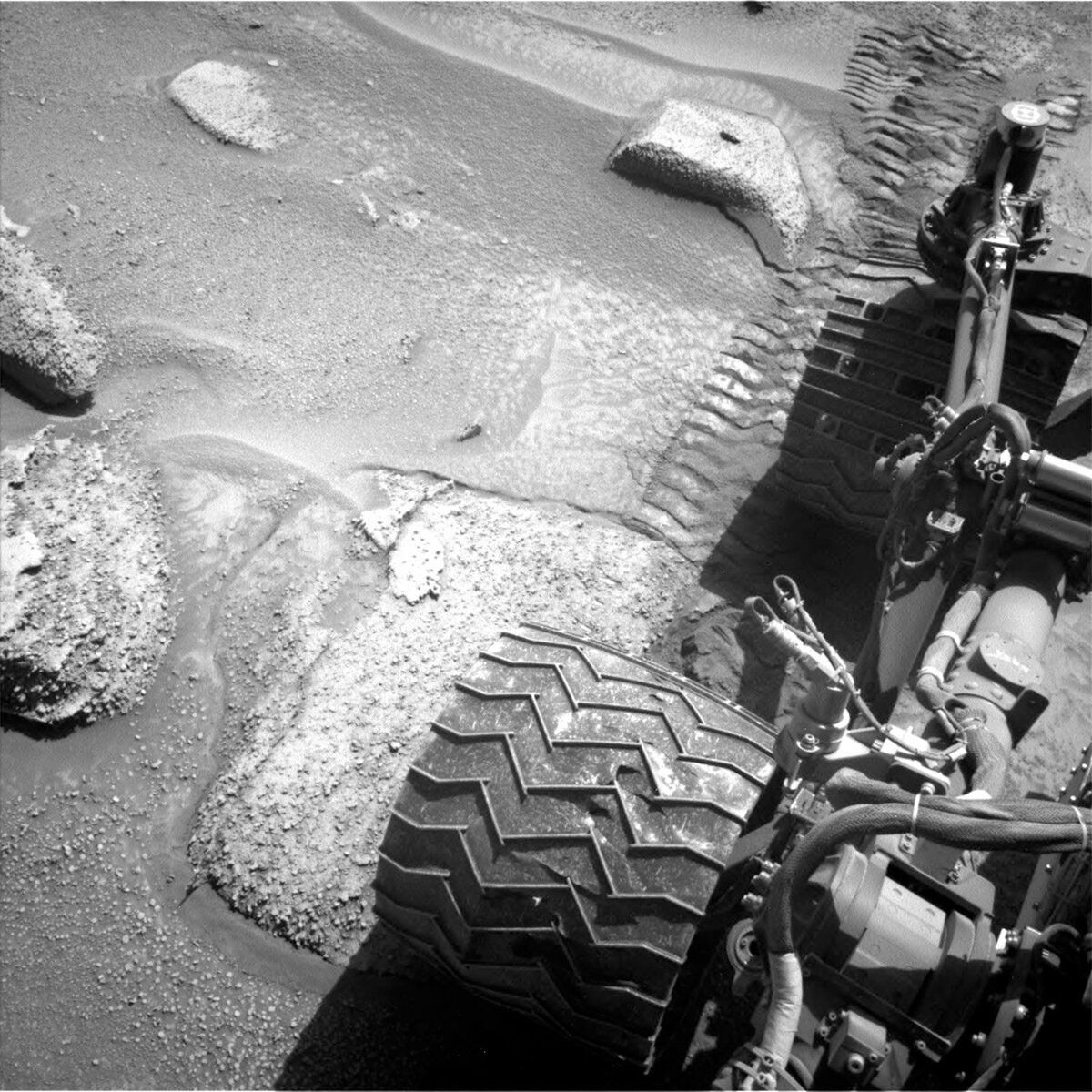
Previously, Curiosity drove ~38 m, a little short of where we intended to be, so we weren’t too sure about the stability of the rocks we were perched on. Due to this, the arm could not be used (better to be safe than sorry). But when one door closes, another opens, and we now had ~2.5 hours (!) of science time to fill with remote observations, and the team was not lacking in suggestions including both geological and atmospheric targets.
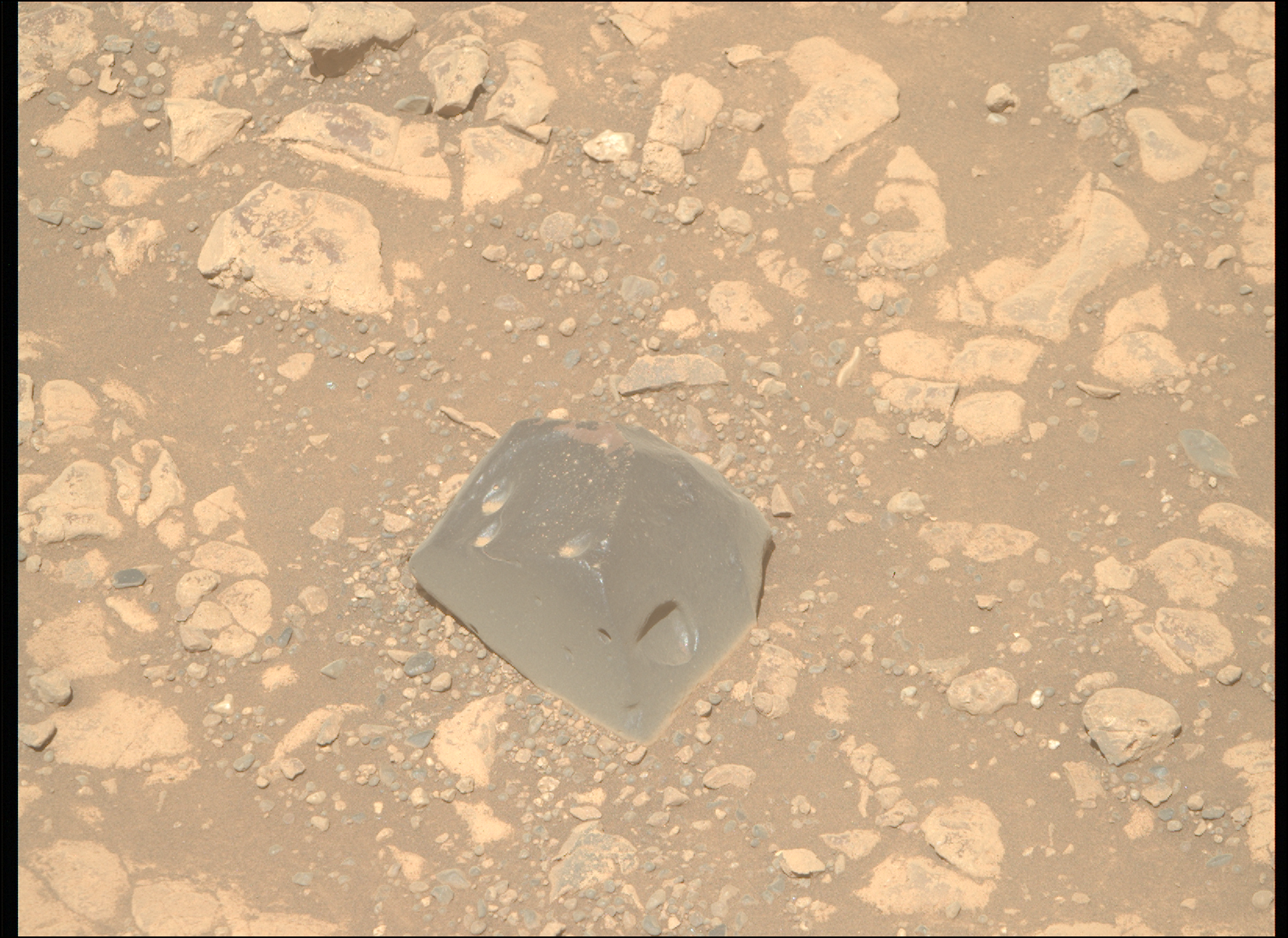
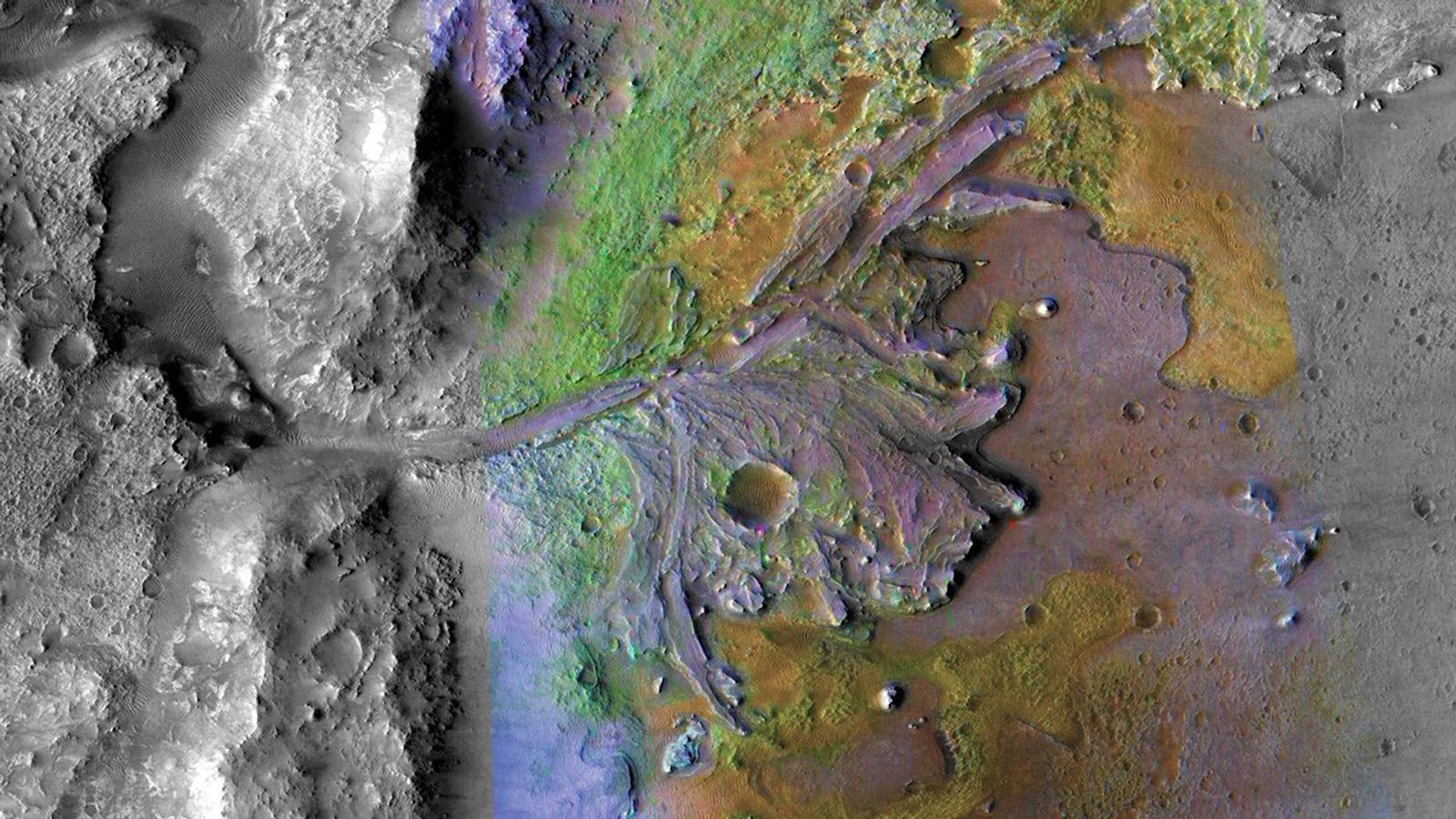
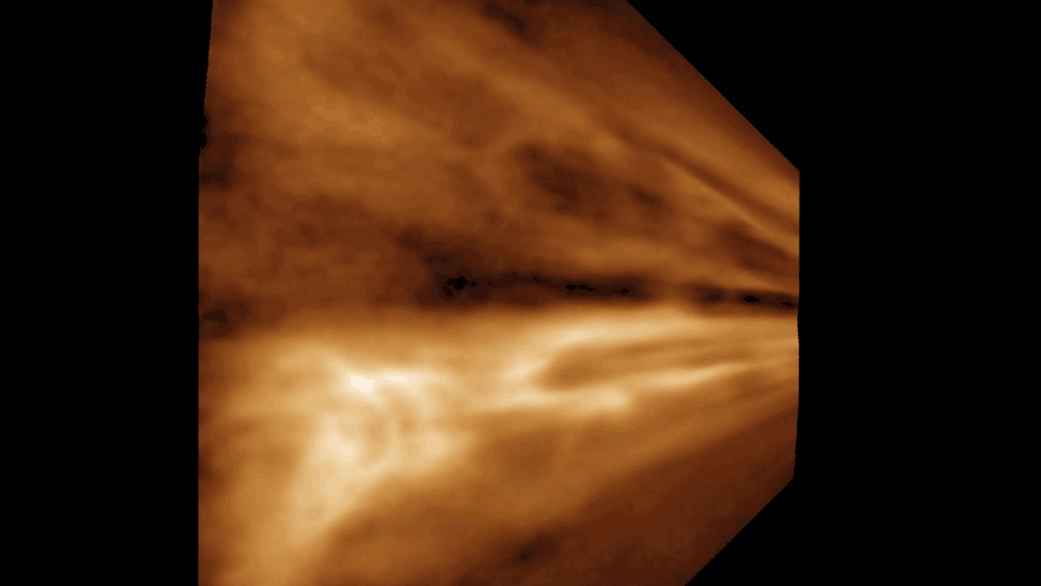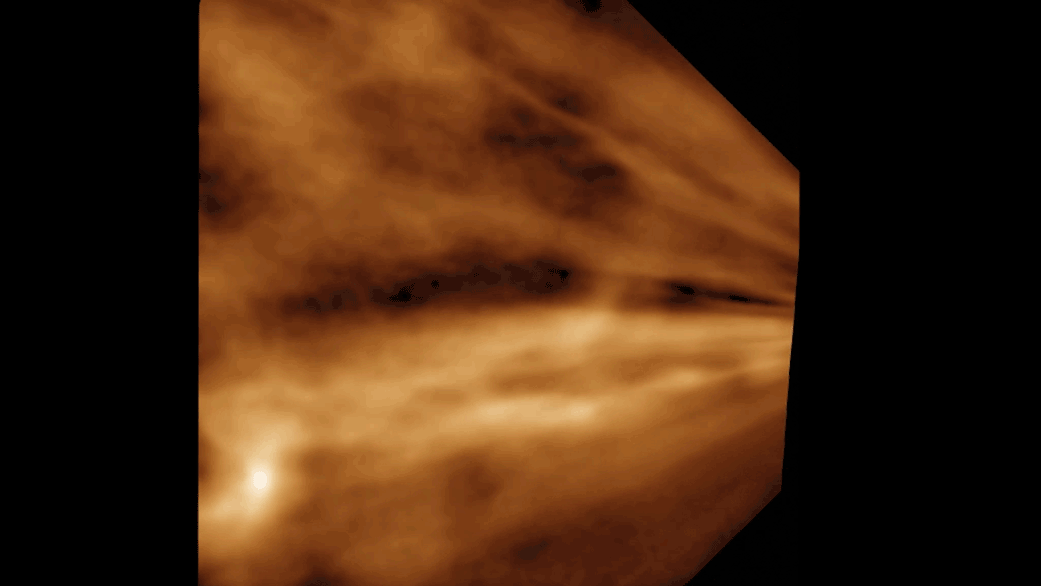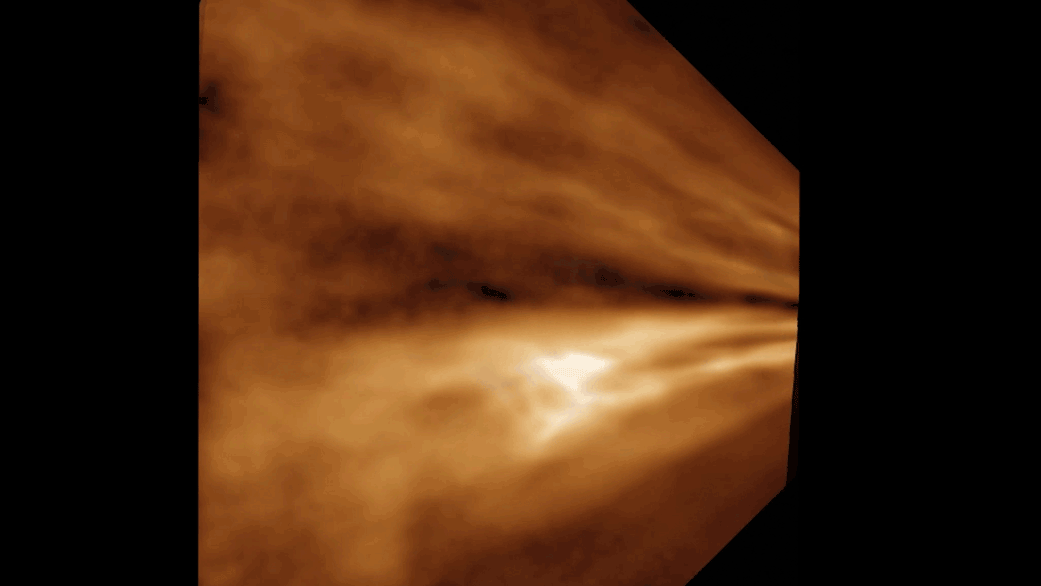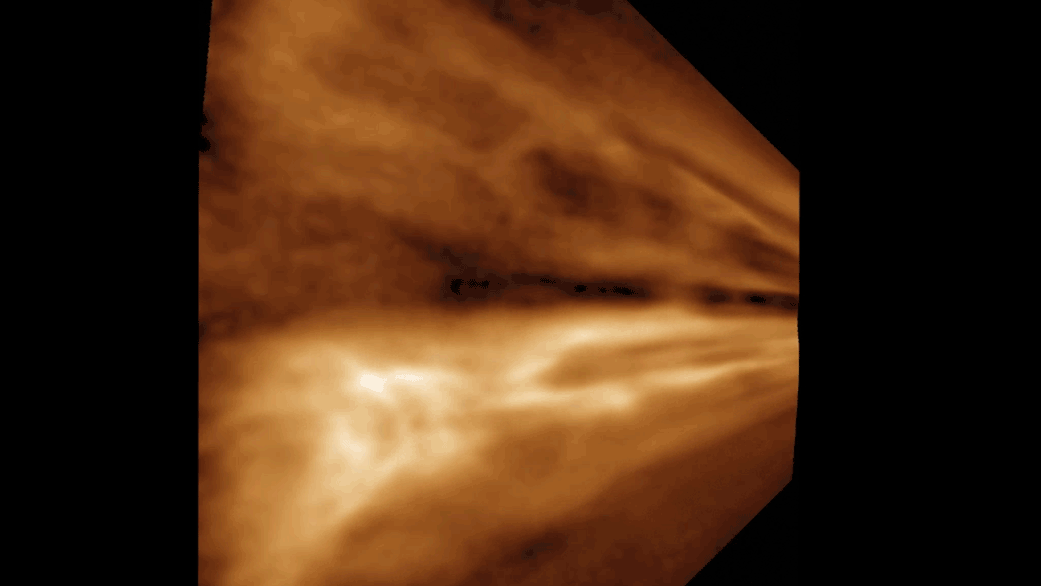
Our science plan starts with MastCam targeting a small, flat rock near the rover named “Crique Guillaume.” Next, ChemCam will take a LIBS of a bedrock target “Lago Do Boto,” before looking backwards for a long-distance RMI towards the NW rim of Gale crater to a sediment fan known as “Peace Vallis.” Curiosity will continue to analyse the surrounding geology with a MastCam target to complement the ChemCam LIBS target “Lago Do Boto.” The team noticed Curiosity had slightly dislodged a rock with one of its wheels so we are targeting this, aptly named “Disturbed Rock.” MastCam will then spend 30 minutes imaging a massive 30x2 mosaic of the ridge we are driving along known as “Starboard Ridge.” Finally, looking backwards we can see a U-shaped “Canyon Lip.” A MastCam target here will be used to assess aeolian erosion. Within this plan, there are ~40 minutes of atmospheric observations too. This includes a Navcam dust devil survey, and a ~30 minute ‘passive sky’ observation using ChemCam to detect trace gases in the atmosphere. The plan ends with a hopeful 17 m drive, taking us even further east on our reroute.
Written by Emma Harris, Graduate Student; Natural History Museum; London, UK