All Mars Resources
Filters

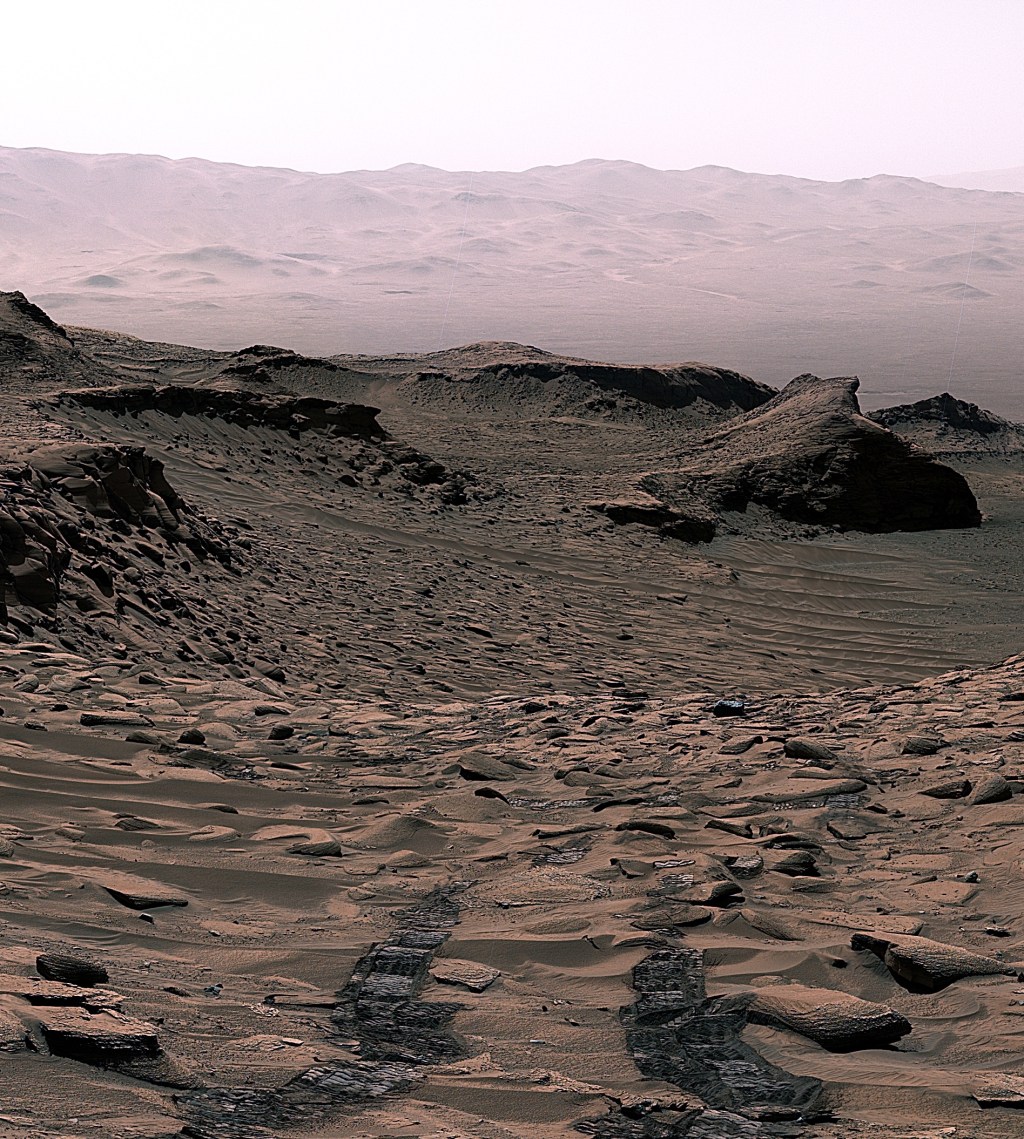
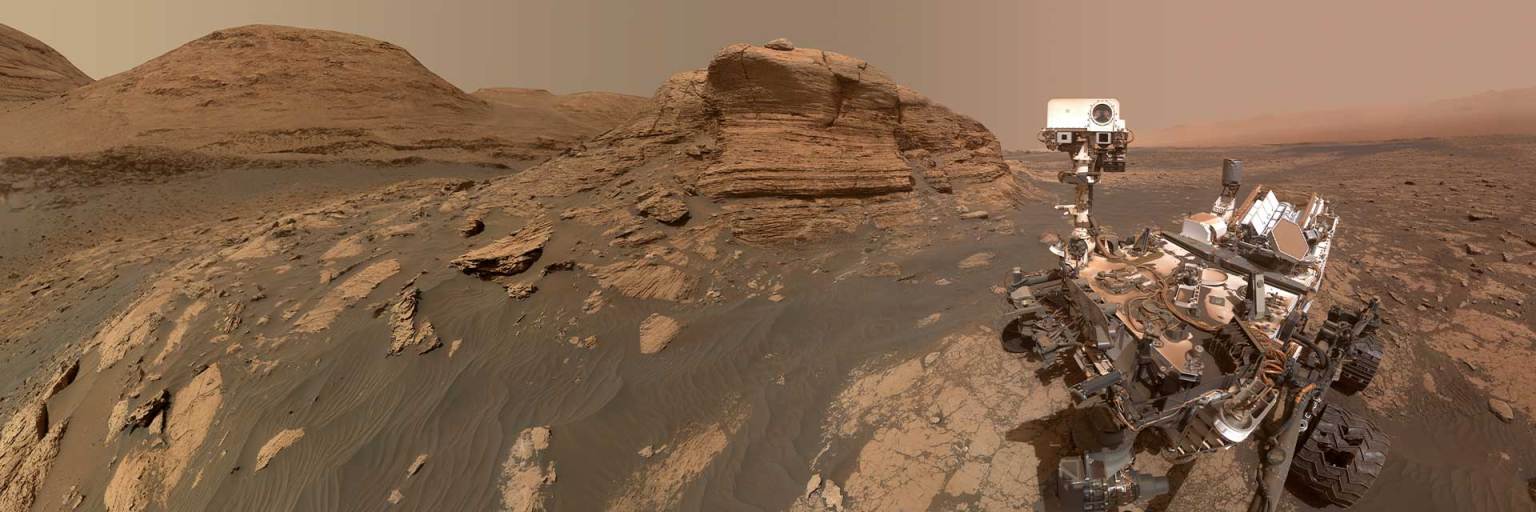
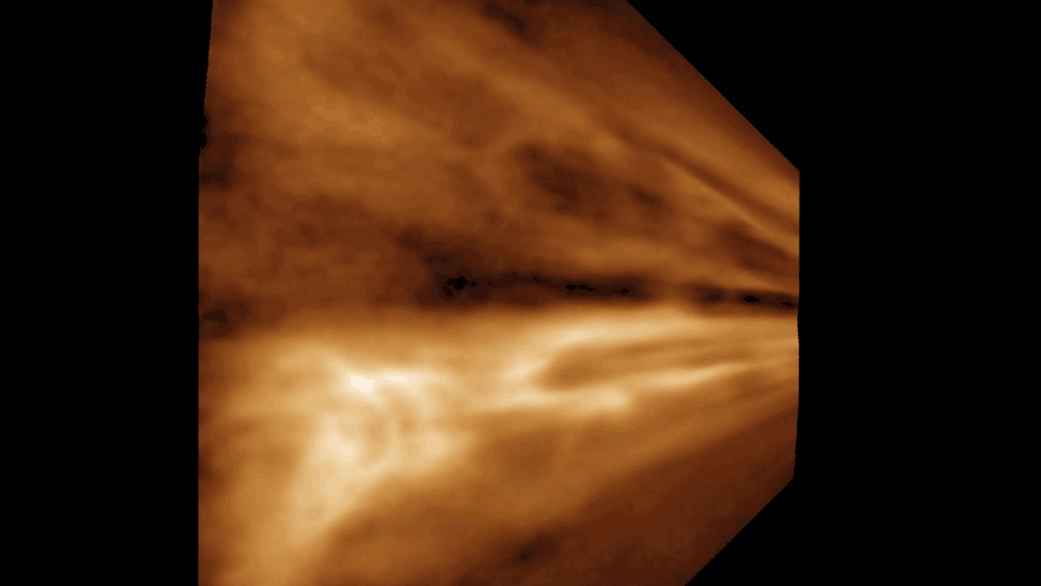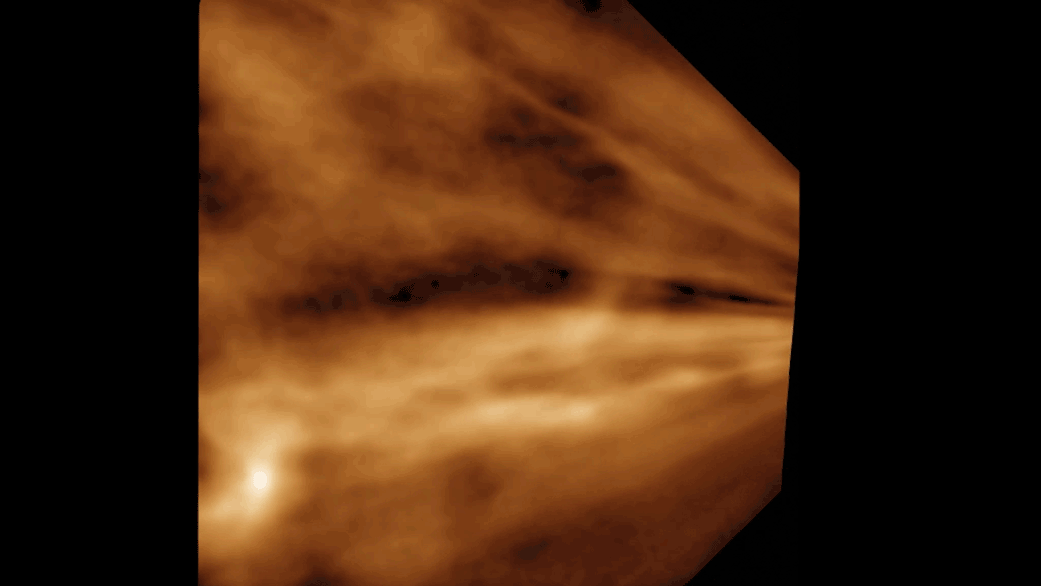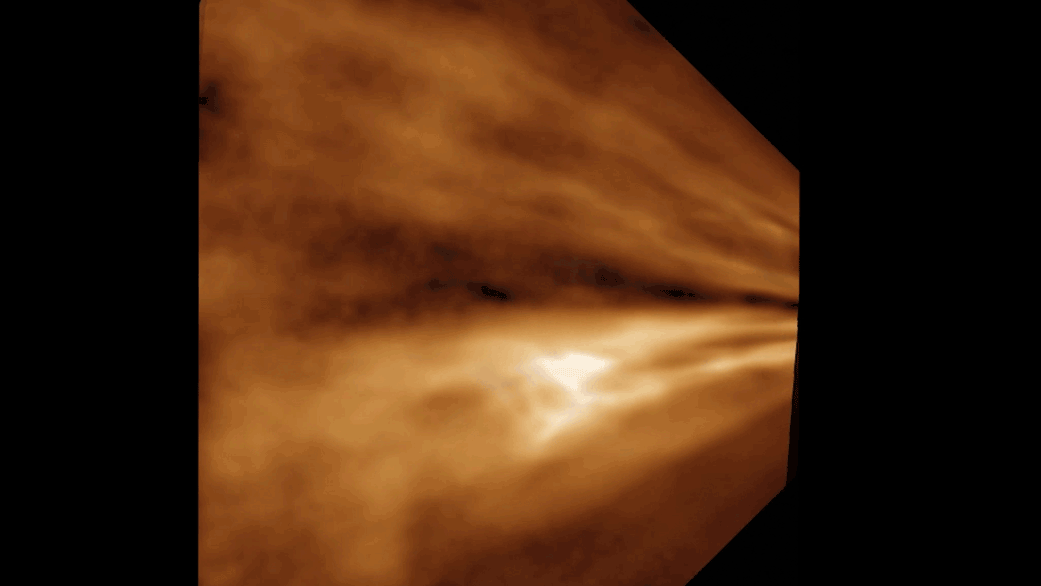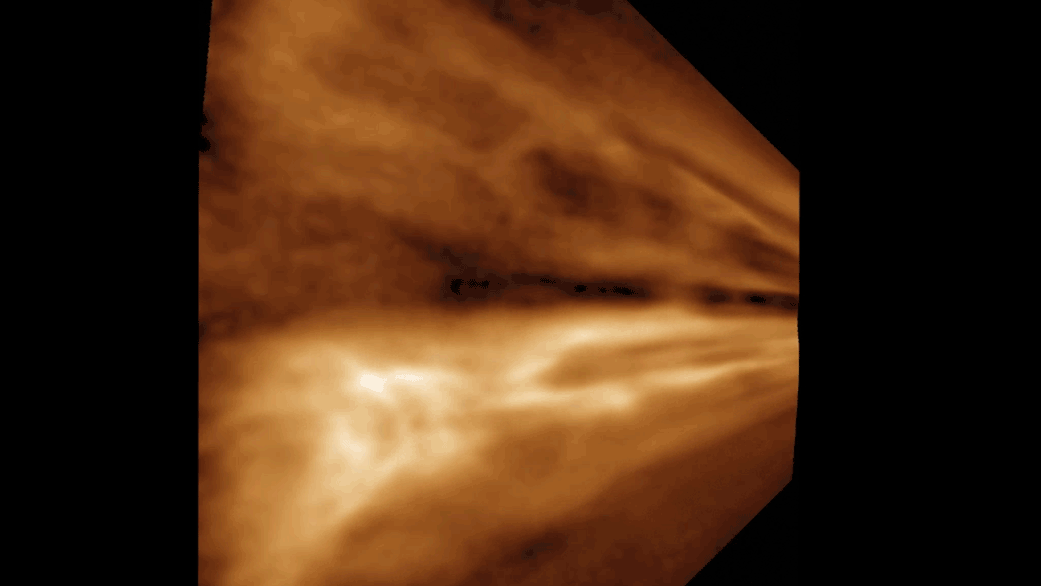
Curiosity took 31 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this mosaic. The seam-corrected…

Curiosity took 31 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this mosaic. The seam-corrected…

Curiosity took 49 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this mosaic. The seam-corrected…

Curiosity took 34 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this mosaic. The seam-corrected…

Curiosity took 26 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this mosaic. The seam-corrected…

Curiosity took 31 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this mosaic.

Meet the 25th Martian sample collected by NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover – “Sapphire Canyon” – a sample taken from a…

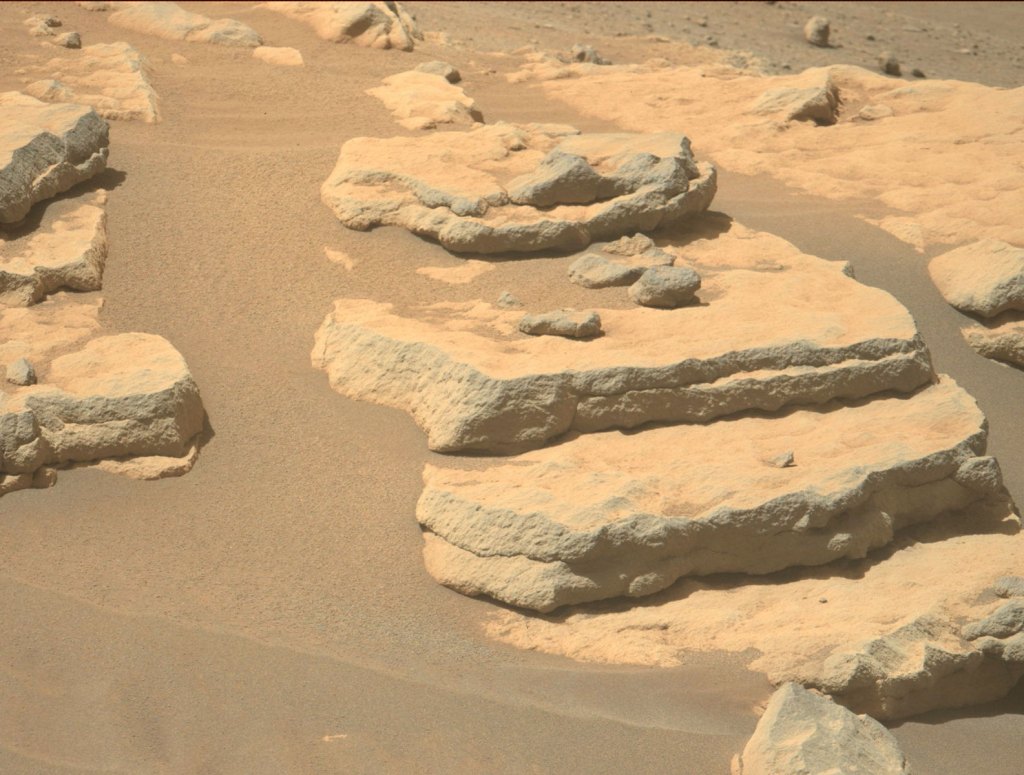
Curiosity took the images on April 02, 2025, Sol 4498 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 2292, site…

Curiosity took the images on March 31, 2025, Sol 4496 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 2214, site…

Curiosity took the images on March 28, 2025, Sol 4493 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 1812, site…

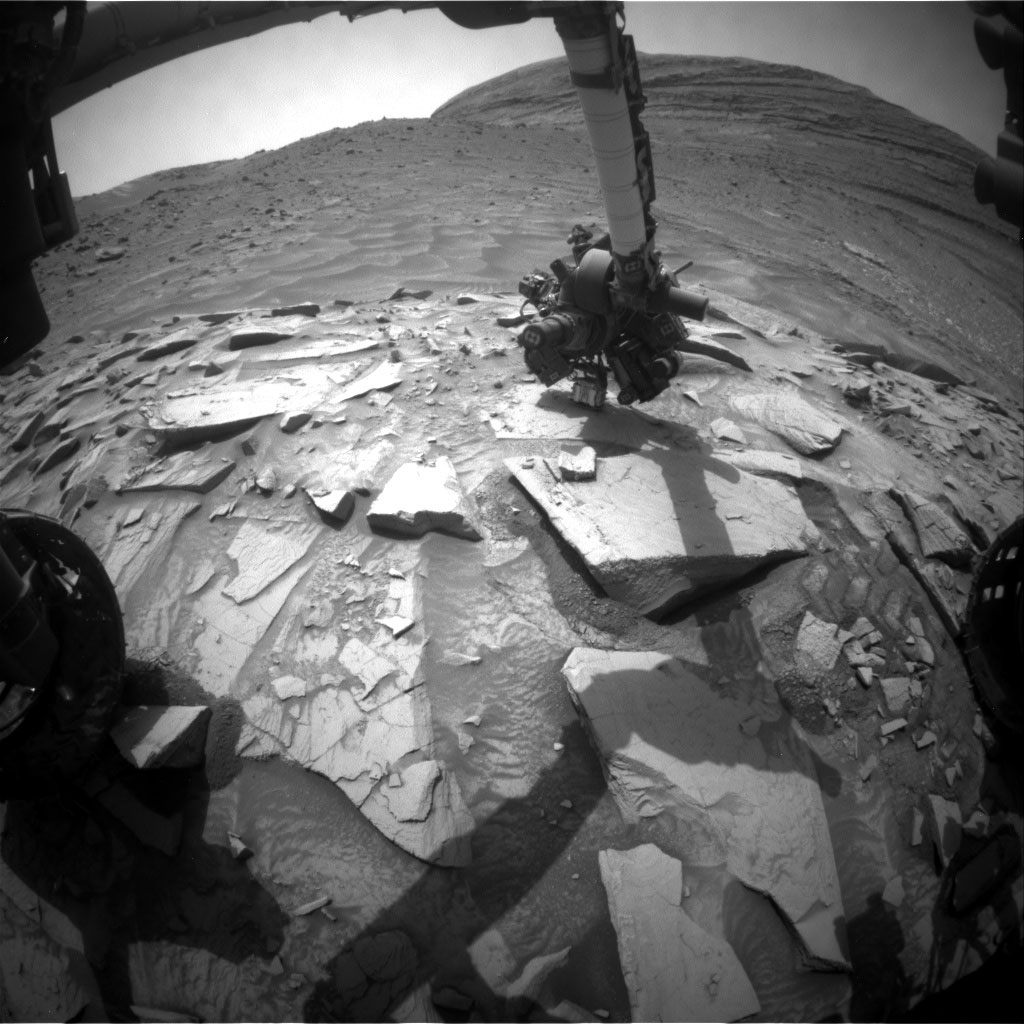
Curiosity took the images on March 26, 2025, Sol 4491 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 1560, site…

Curiosity took the images on March 24, 2025, Sol 4489 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 1380, site…

Curiosity took the images on March 22, 2025, Sol 4487 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 1164, site…

Curiosity took the images on March 19, 2025, Sol 4484 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 918, site…

Curiosity took the images on March 17, 2025, Sol 4483 of the Mars Science Laboratory mission at drive 780, site…