A Geologic Model for Eridania Basin on Ancient Mars
| Credit | Image credit: NASA |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
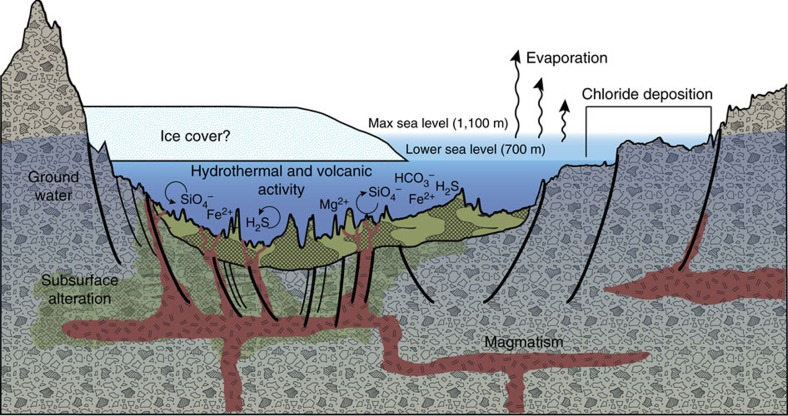
This diagram illustrates an interpretation for the origin of some deposits in the Eridania basin of southern Mars as resulting from seafloor hydrothermal activity more than 3 billion years ago.
The ground level depicted is an exaggerated topography of a transect about 280 miles (450 kilometers) long. Blue portions of the diagram depict water-depth estimates and the possibility of ice covering the ancient sea.
Thick, clay-rich deposits (green) formed through hydrothermal alteration of volcanic materials in deep water, by this model. Notations indicate deep-water reactions of iron and magnesium ions with silicates, sulfides and carbonates. Deep-seated structural discontinuities could have facilitated the ascent of magma from a mantle source. Chloride deposits formed from evaporation of seawater at higher elevations in the basin.
This graphic was included in a 2017 report "Ancient hydrothermal seafloor deposits in Eridania basin on Mars" in Nature Communications.
