All Mars Resources
Filters
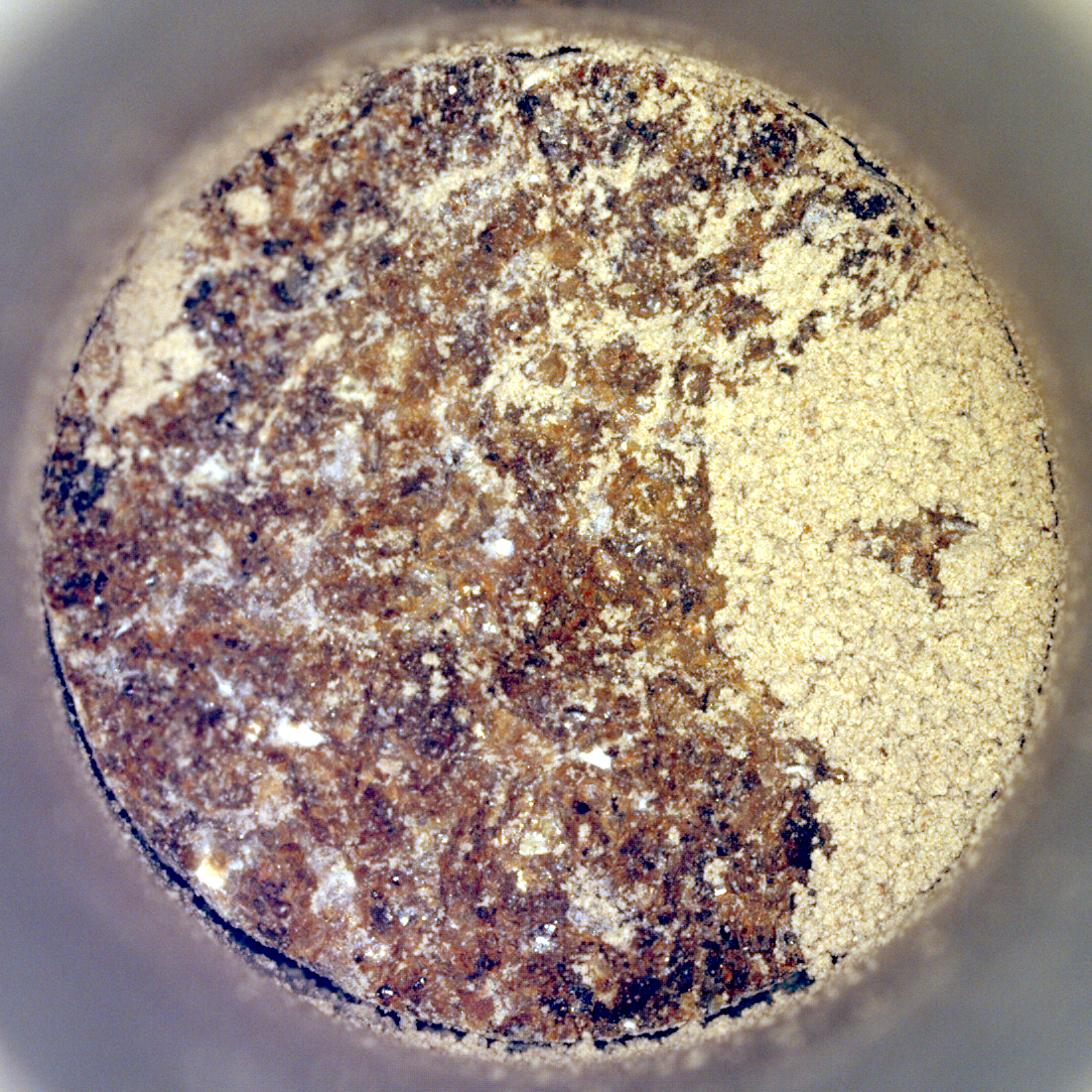

Perseverance’s ‘Bunsen Peak’ Sample
NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover captured this image of a sample cored from a rock called “Bunsen Peak” on March 11,…

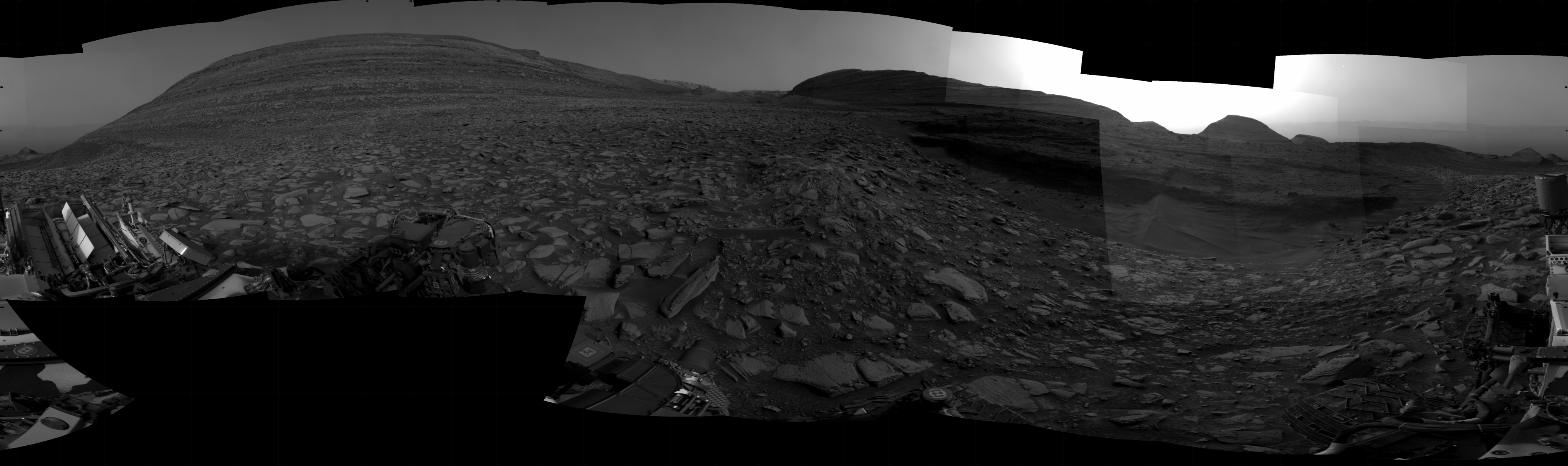
NASA’s Curiosity Rover Reaches Gediz Vallis Channel (360 View)
360-degree panorama provided by NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover. This view was captured at Gediz Vallis channel, a feature that formed…
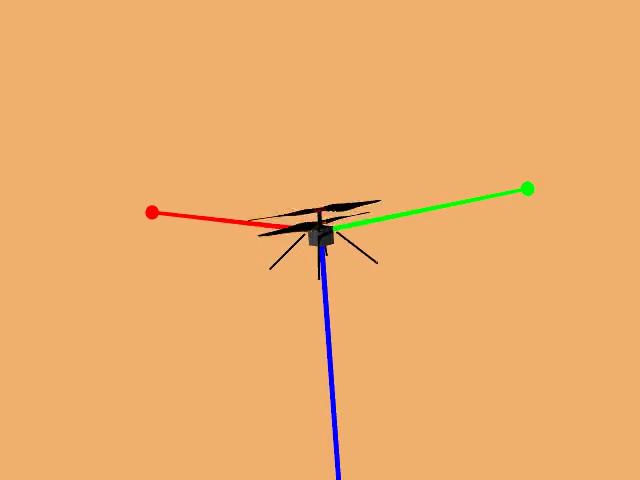
Animation of Mars Helicopter Flight Test
This animation shows a simulation of the response of NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter to the system identification, or “Sys-ID,” process.…
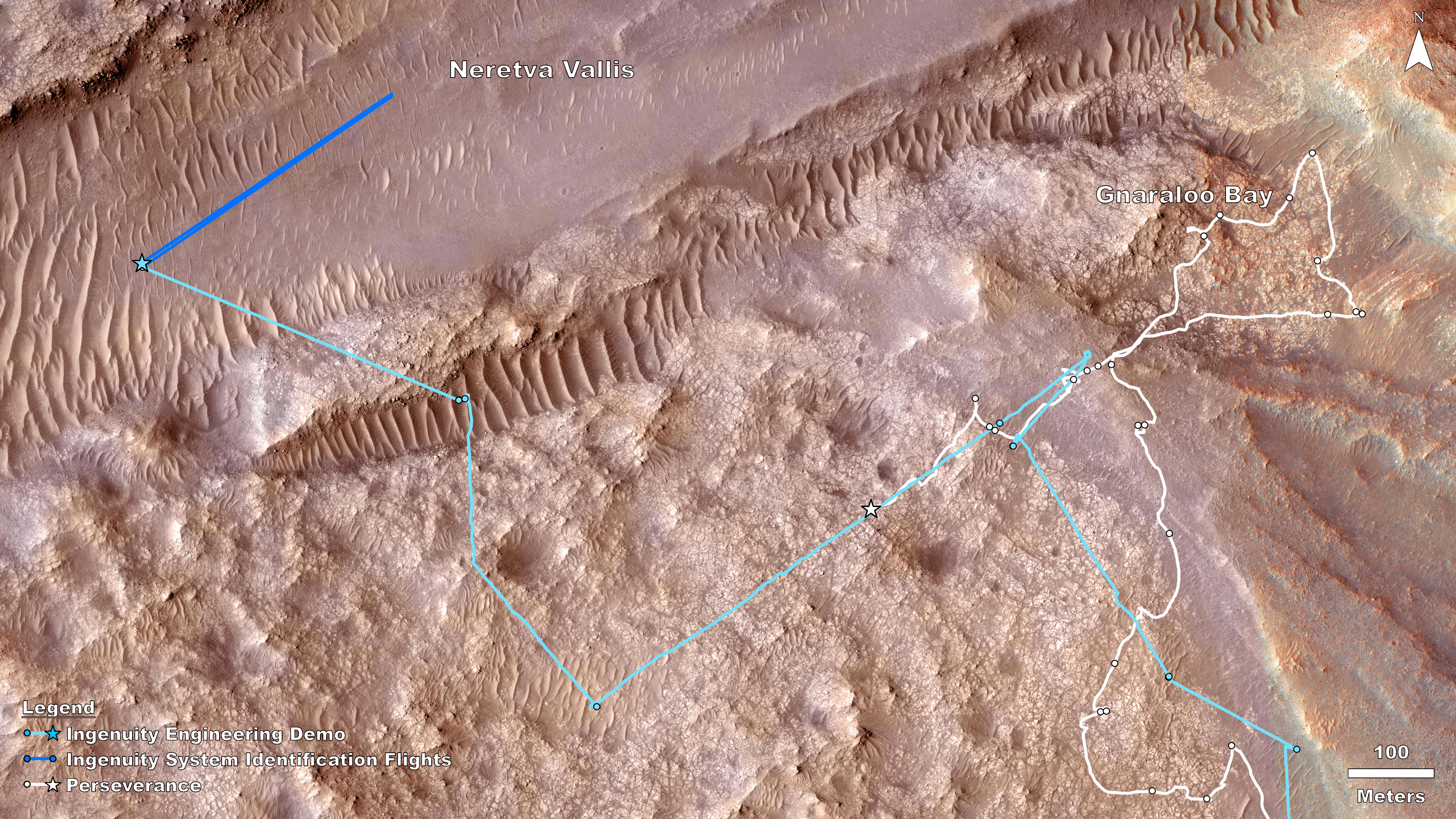
Rover, Helicopter Locations in Jezero Crater
This map shows the locations of NASA’ Perseverance rover (white star) and Ingenuity Mars Helicopter (cyan star) on Dec. 19,…

Sol 4132: Right Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Projection
NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity took 31 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4130: Right Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Projection
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 31 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4128: Right Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Perspective
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 30 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…
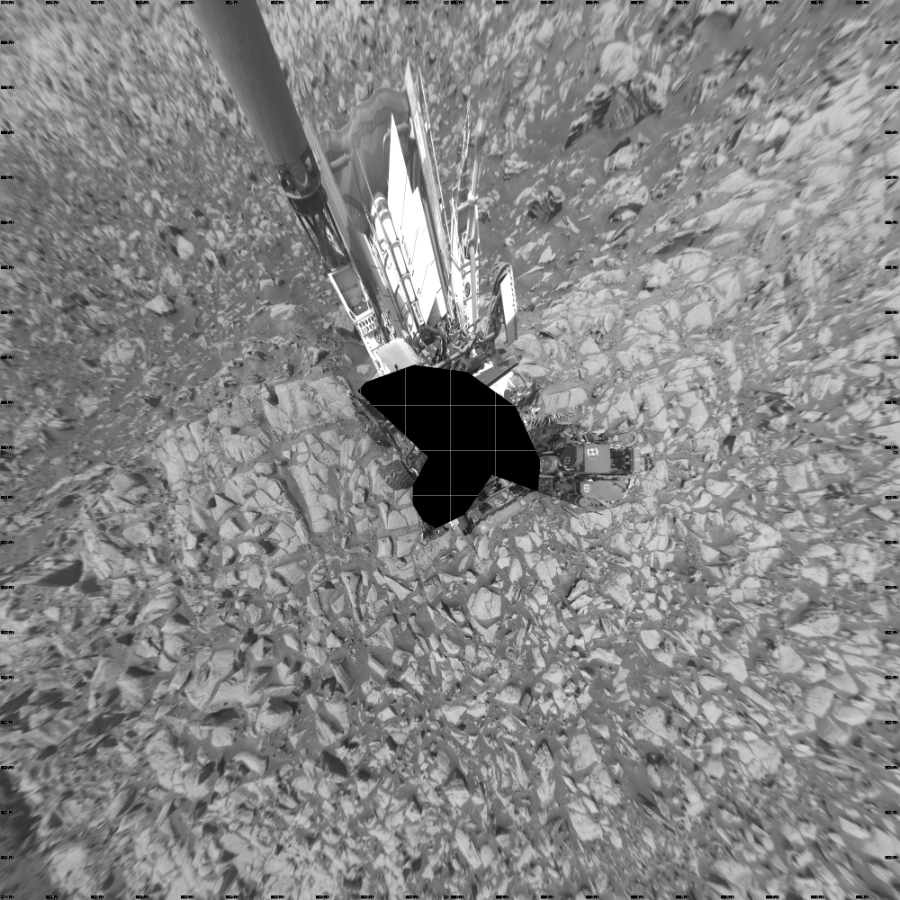

Sol 4128: Left Navigation Camera, Vertical Projection
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 30 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Left Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4128: Left Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Perspective
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 30 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Left Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4128: Left Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Projection
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 30 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Left Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4128: Mast-Mounted Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Perspective
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 30 image pairs in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4128: Right Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Projection
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 31 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4125: Right Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Projection
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 52 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4123: Right Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Projection
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 51 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…

Sol 4118: Right Navigation Camera, Cylindrical Projection
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity took 49 images in Gale Crater using its mast-mounted Right Navigation Camera (Navcam) to create this…
