An Expanse for Perseverance to Explore

| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS |
|---|---|
| Language |
|


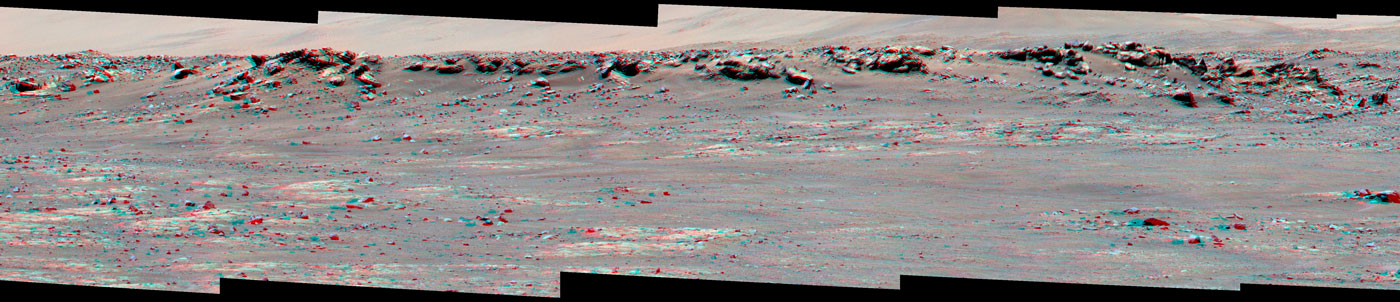
An Expanse for Perseverance to Explore
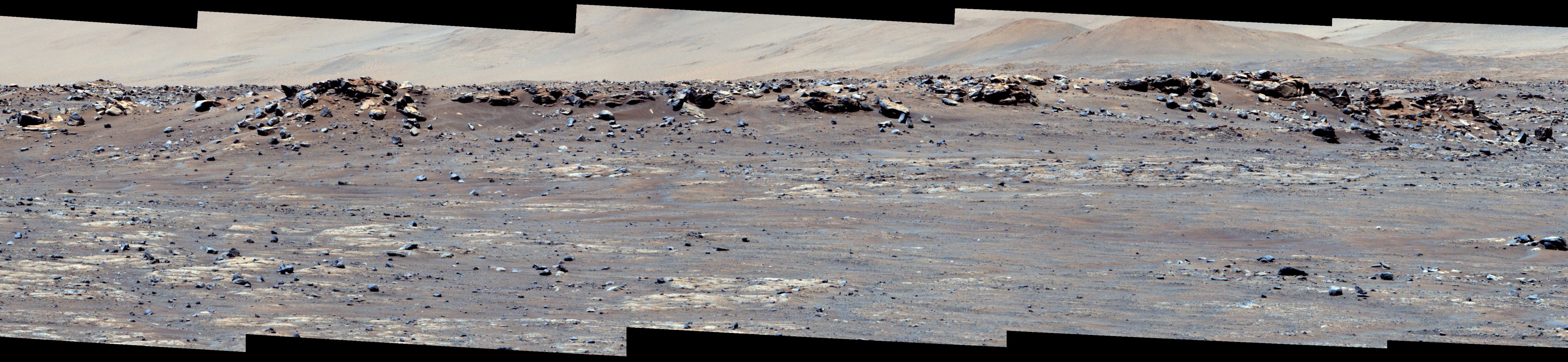
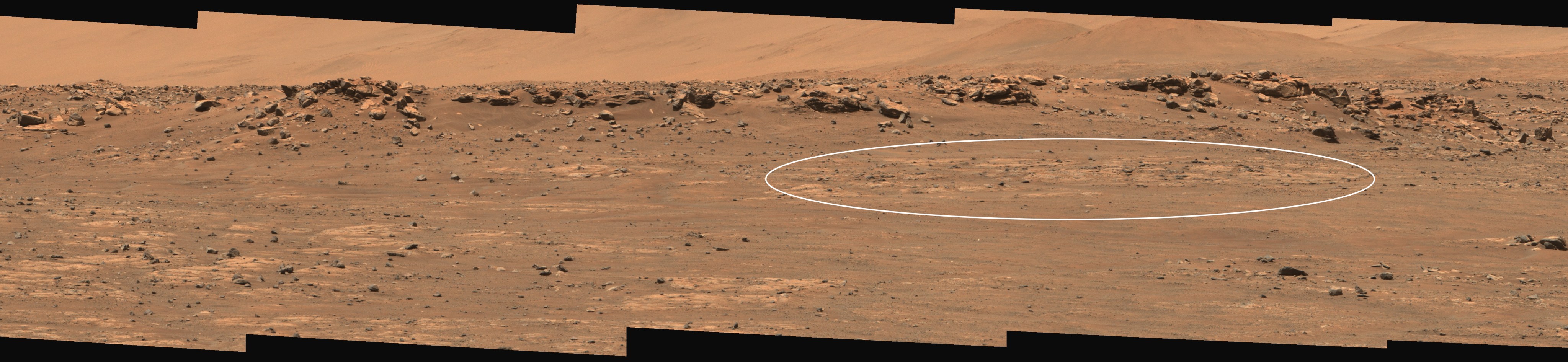
This wide view of Mars’ Jezero Crater was taken by NASA’s Perseverance rover on July 15, 2021 (the 143rd sol, or Martian day, of its mission). The rover has driven nearly a mile (1.5 kilometers) south of its landing site, “Octavia E. Butler Landing,” into a region the team has nicknamed the “Crater Floor Fractured Rough” unit. The stones that appear light-colored and flat in this image are informally referred to as the “paver rocks” and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view.
Five images from the rover’s Mastcam-Z instrument were calibrated and combined to make this mosaic. One version, presented in natural color, simulates the approximate view that we would see with our own eyes if we were there. Another version is presented in enhanced color to exaggerate the subtle red, green, and blue color differences among the materials in this scene.
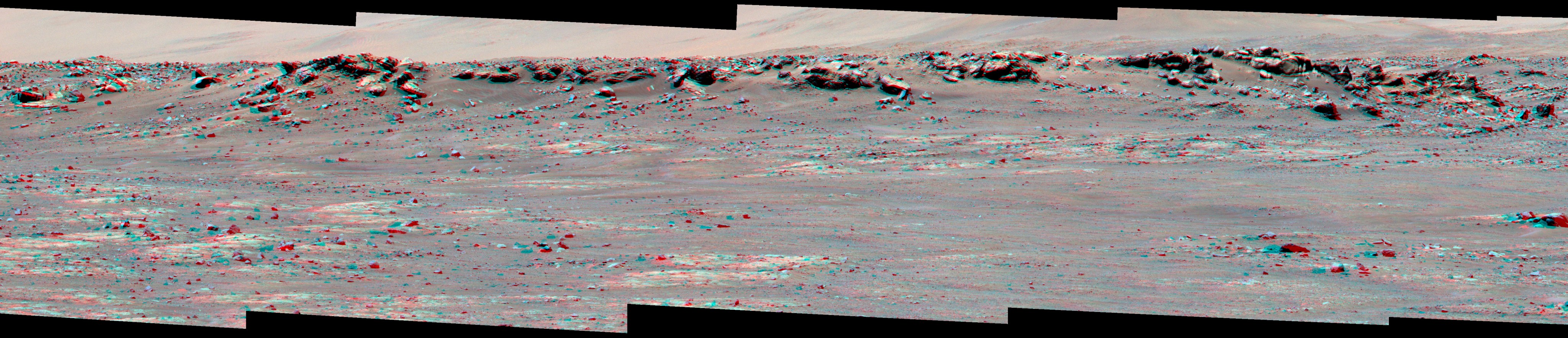
A third version combines the five images from both the left and right Mastcam-Z cameras into an anaglyph (for red-blue glasses) that simulate a 3D view of the scene in enhanced color.
Perseverance has been exploring the floor of Jezero since landing on Feb. 18, 2021.
The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets.
A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA’s Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
Subsequent missions by NASA in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency) would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these cached samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California built and manages operations of the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover for NASA.
For more information about the mission, go to: https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020




