Fortun Ridge’ Imaged on Ingenuity’s Flight 27
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
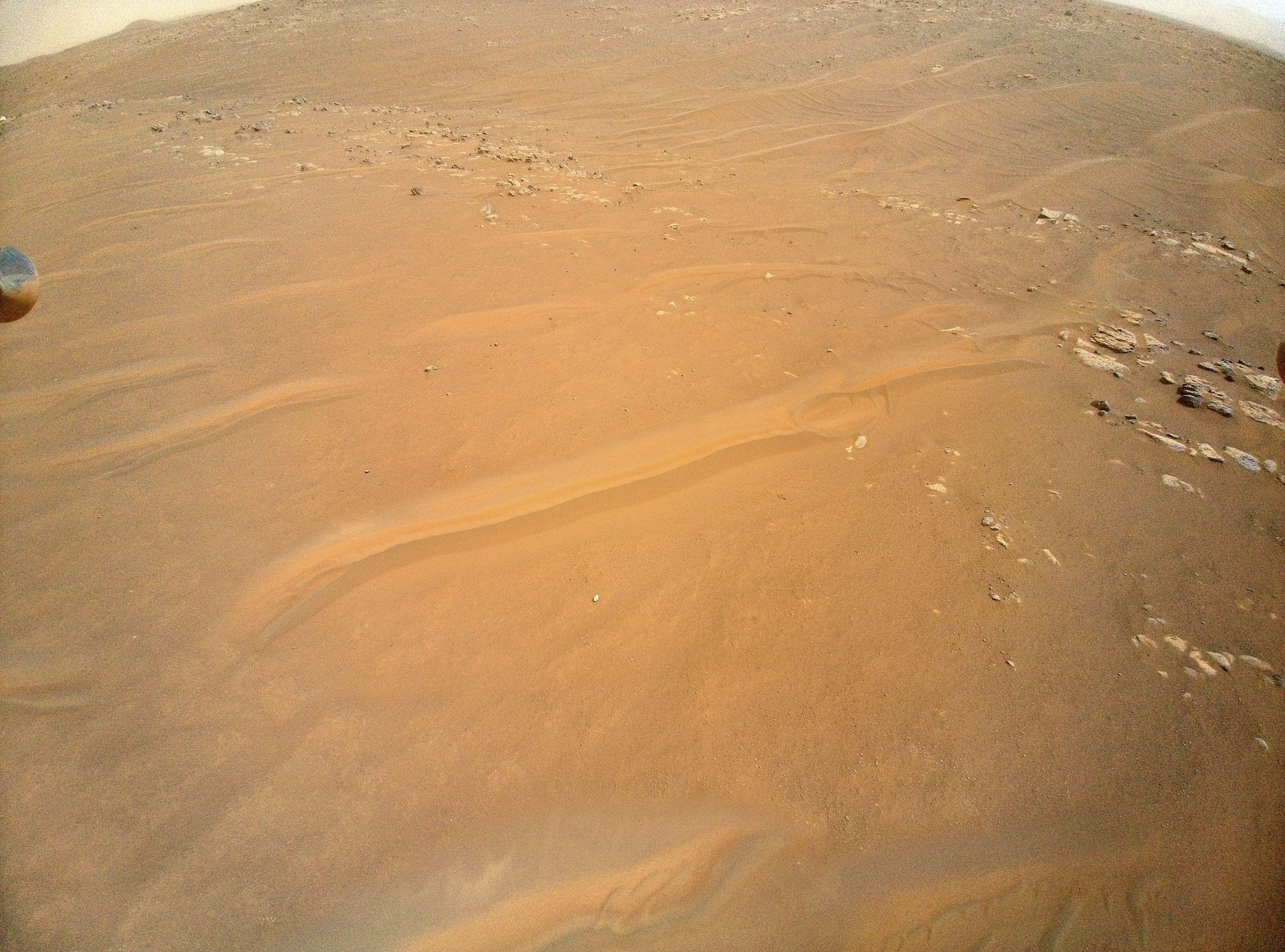
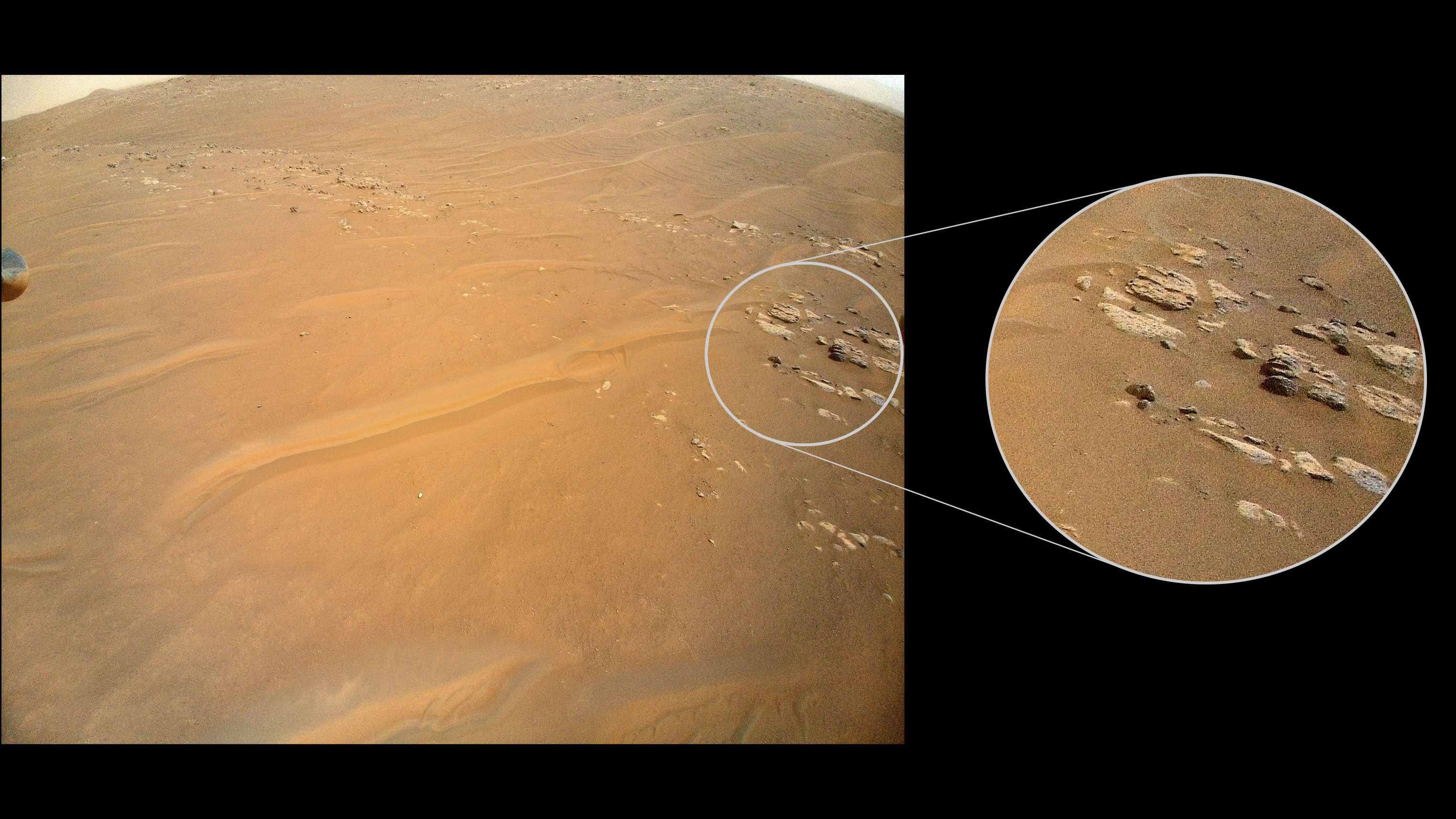
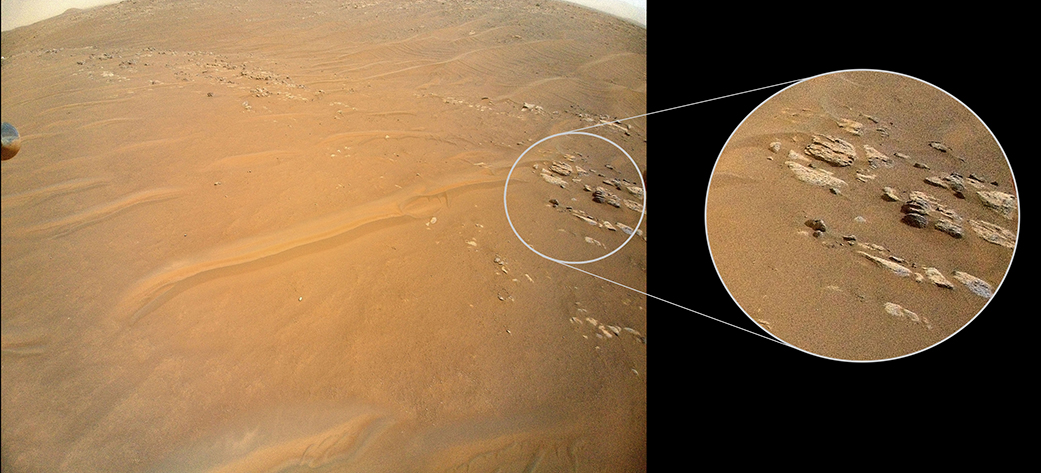
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter recently surveyed a ridgeline near the ancient river delta in Mars’ Jezero Crater at request of the Perseverance rover’s science team. On the left is the full image Ingenuity acquired of the ridgeline on April 23, 2022, during its 27th flight. The science team calls the line of rocky outcrops running from the upper left to middle right of the main image “Fortun Ridge.” Enlarged at right is a close-up of one of the ridgeline’s rocky outcrops.
This portion of Jezero Crater is of interest to the science team because of the clear exposure of the rocky outcrops that define the boundary between two abutting crater floor geologic units, “Séítah” and “Máaz.” The geology of both units is thought to be of igneous (volcanic) origin.
The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which also manages the project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley, and NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity’s development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System.


