Perseverance’s Route to the Delta
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/USGS/JHU-APL |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
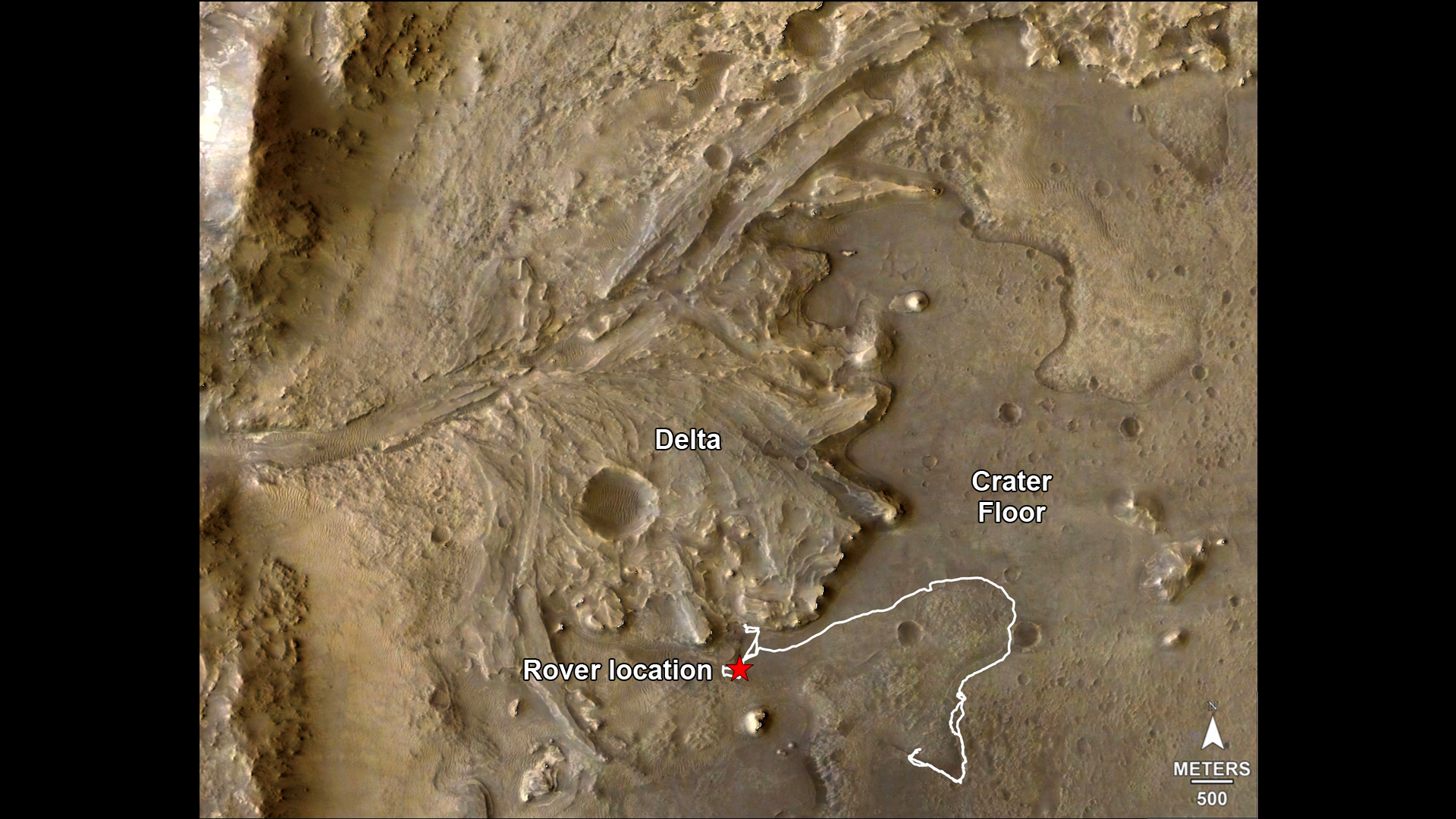
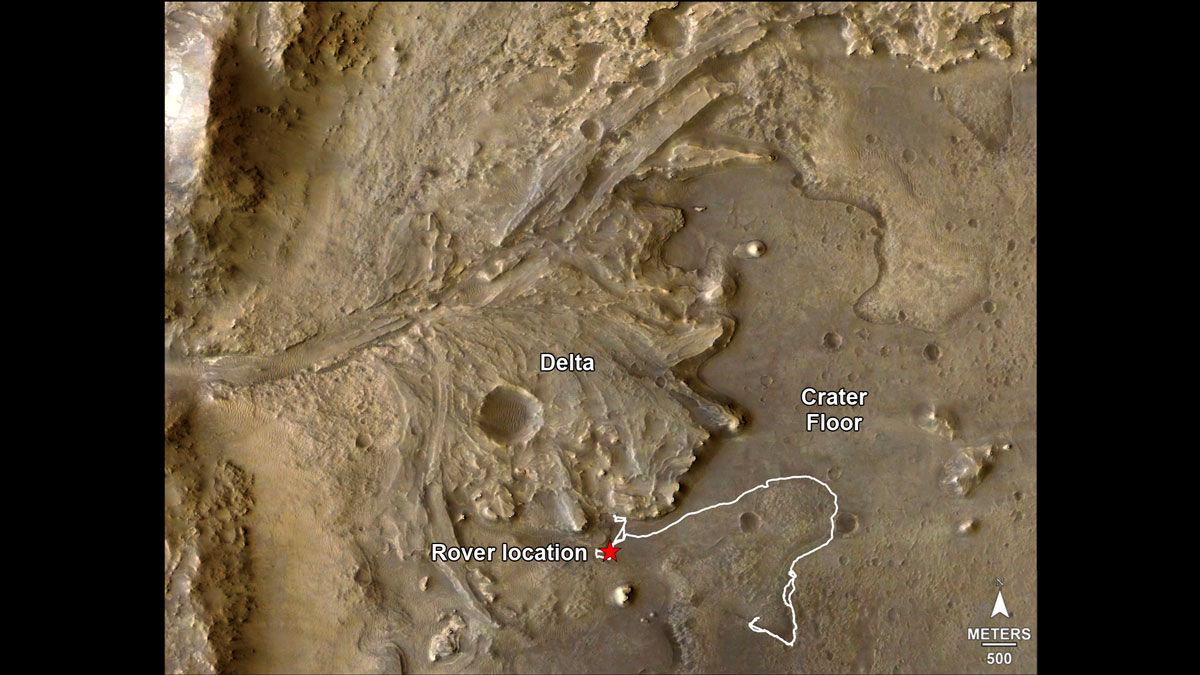
The route of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover – from its landing site on the floor of Jezero Crater to the ancient river delta, which it is currently exploring – is shown in this annotated image composed of overhead views from the agency’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The red star indicates the location of the rover in September 2022.
Perseverance touched down at “Octavia E. Butler Landing” on Feb. 18, 2021, and explored formations (abbreviated “fm” in the annotation) known as “Séítah” and “Máaz” on the floor of Jezero Crater before driving toward the delta region. The delta, which Perseverance reached in April 2022, is a fan-shaped area where, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediment. Scientists consider it one of the best places on Mars to search for potential signs of ancient microbial life.
For this image, the Perseverance team and the U.S. Geological Survey collaborated on the base map, combining multiple images from the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera with color from the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM), both instruments aboard MRO. The HiRISE images used span a period from 2007 to 2017.
A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust).
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA’s Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover.
For more about Perseverance: mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/
JPL manages MRO for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, built and leads the CRISM instrument.