Perseverance Views Drifting Clouds
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
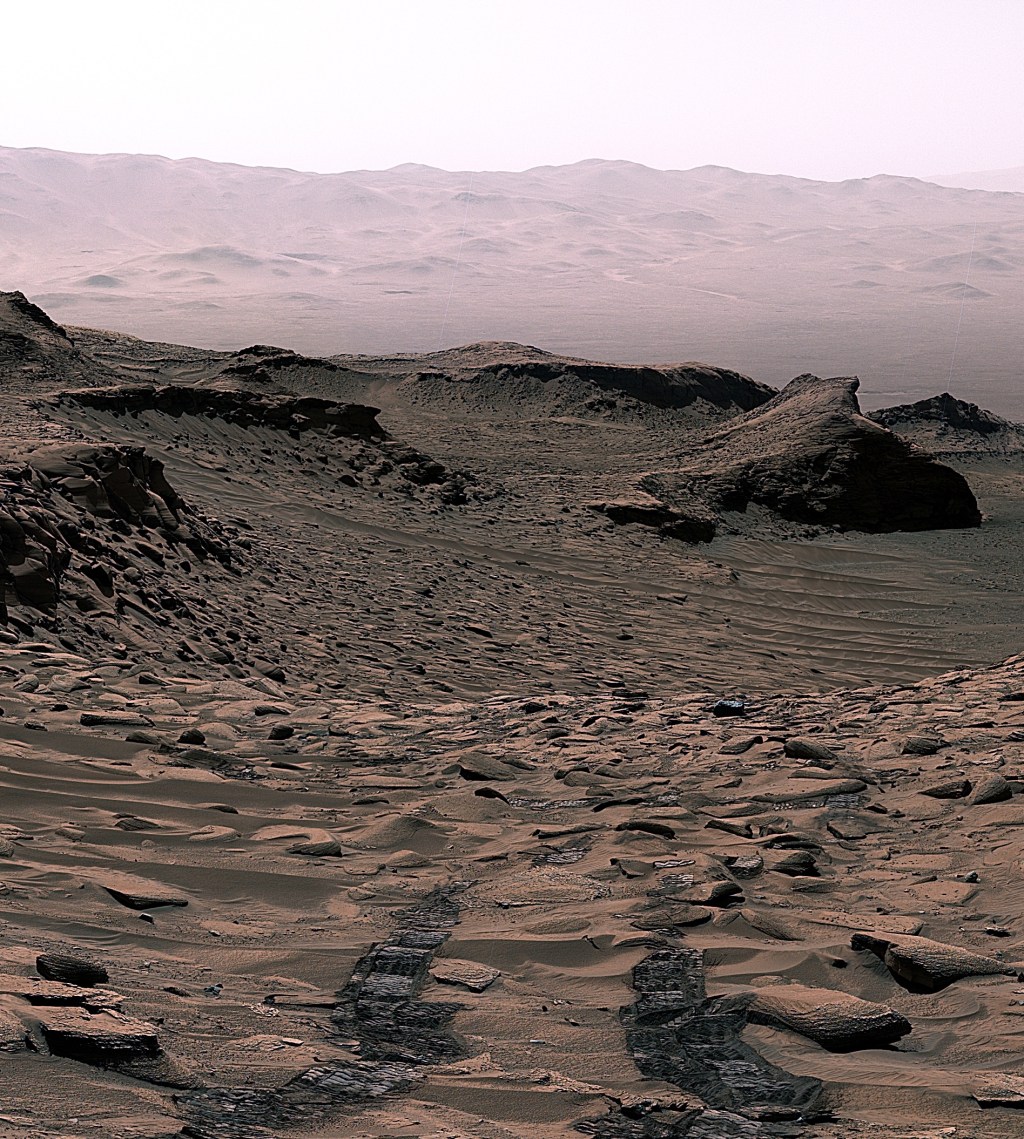
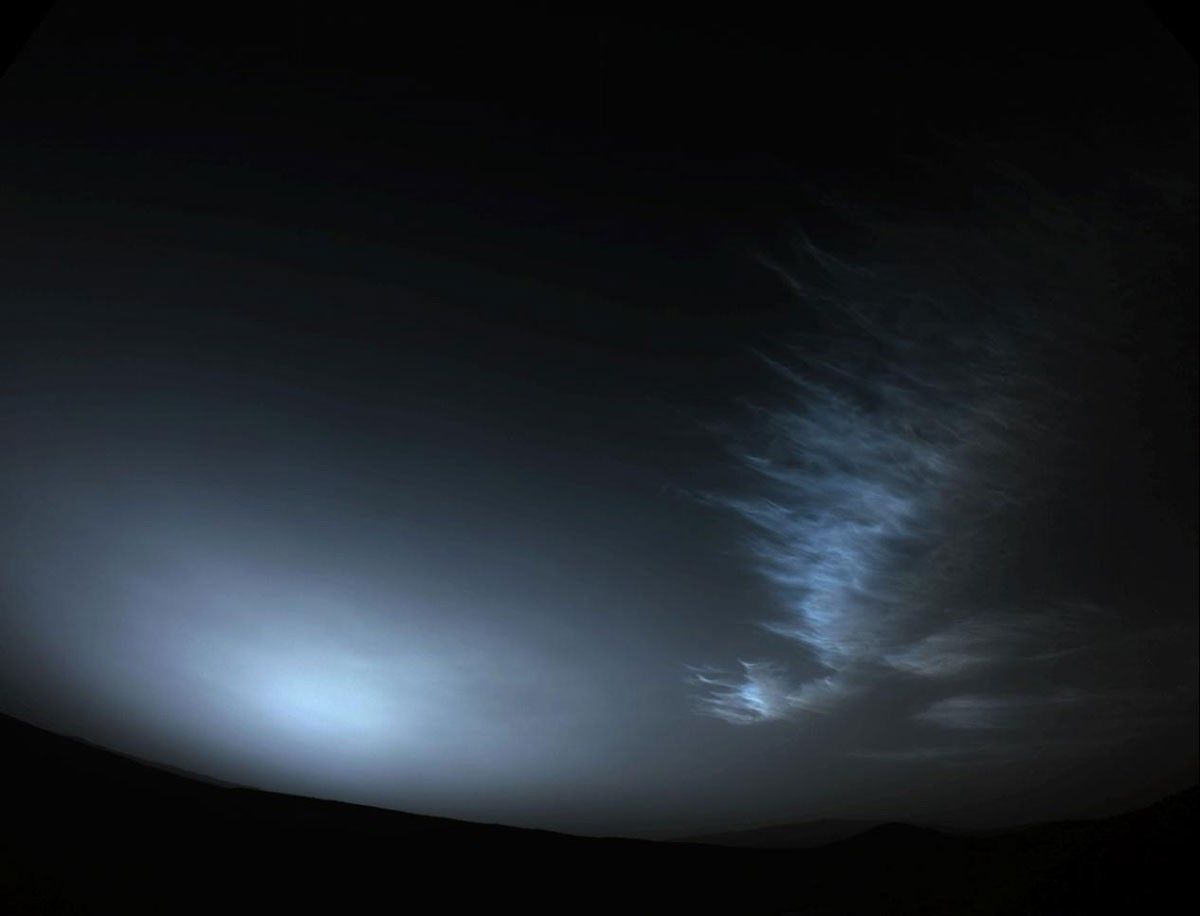
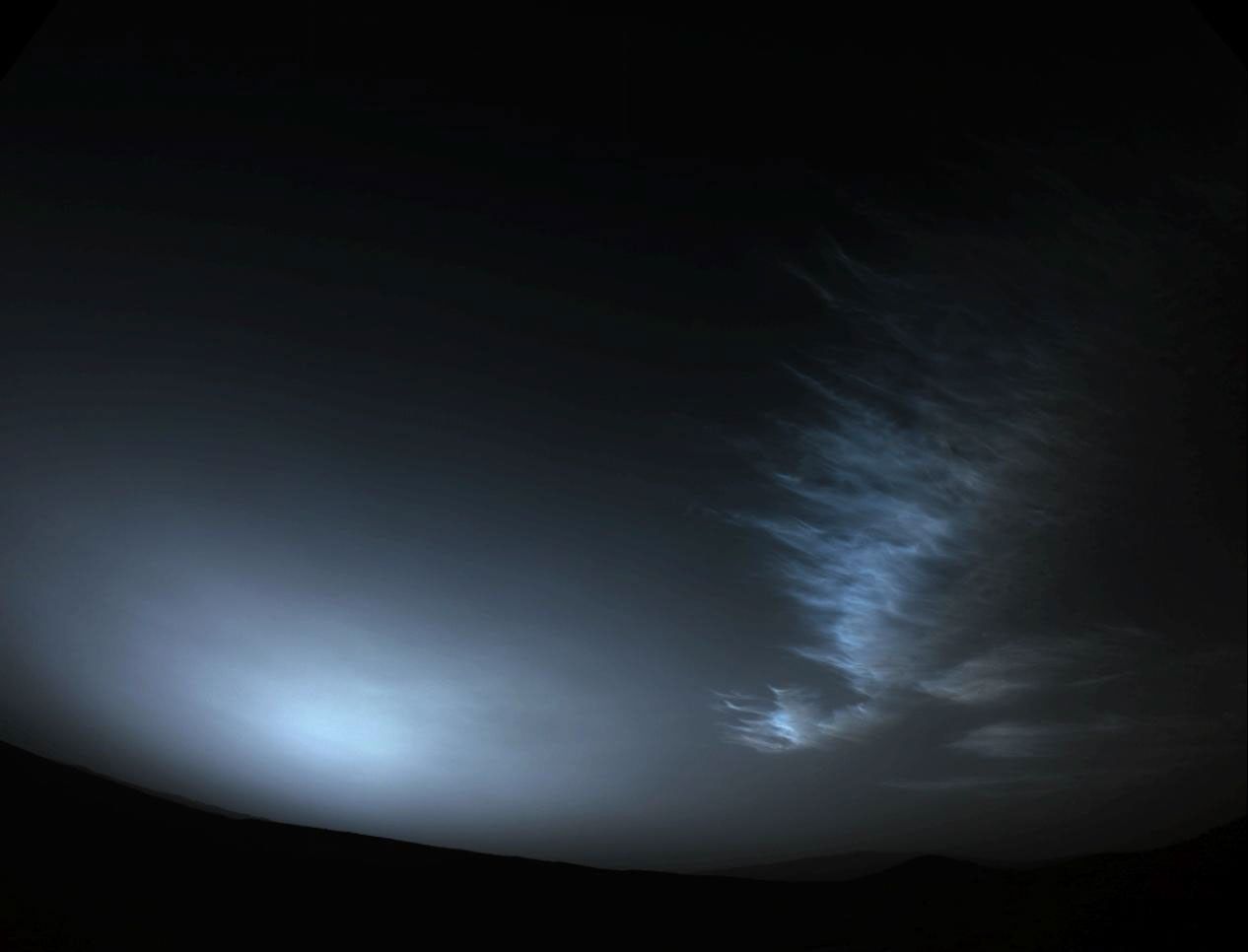
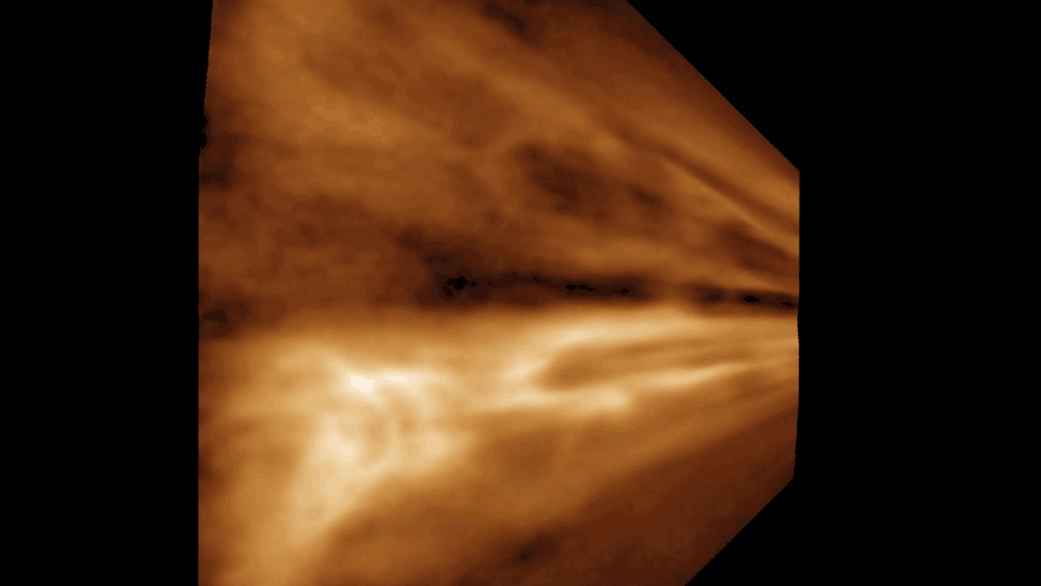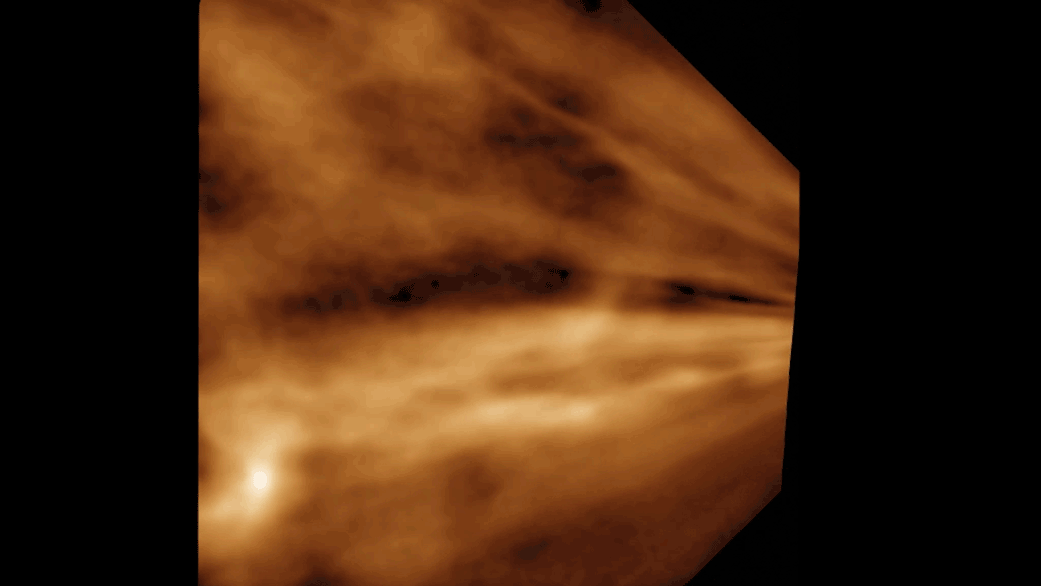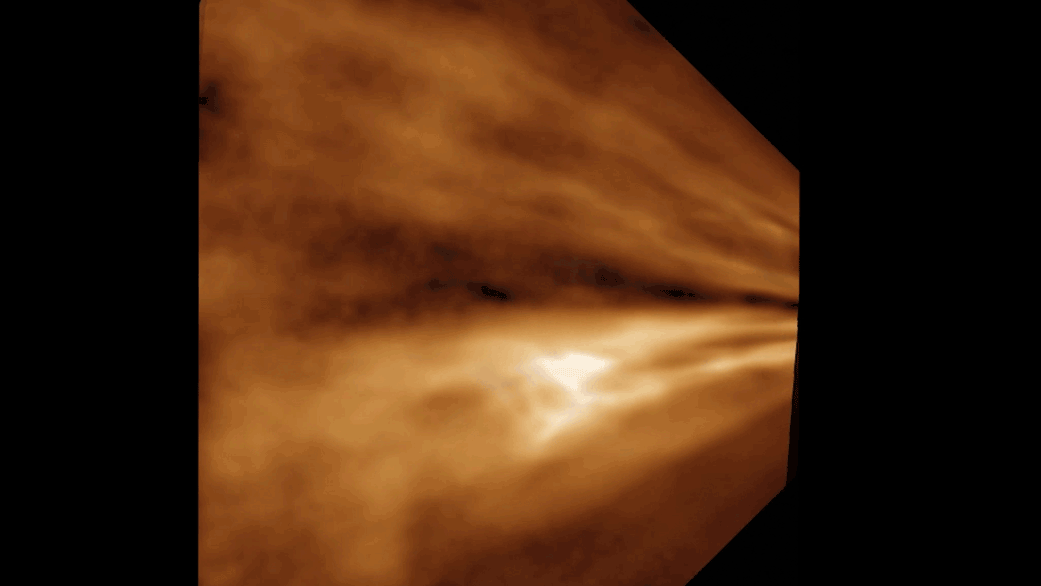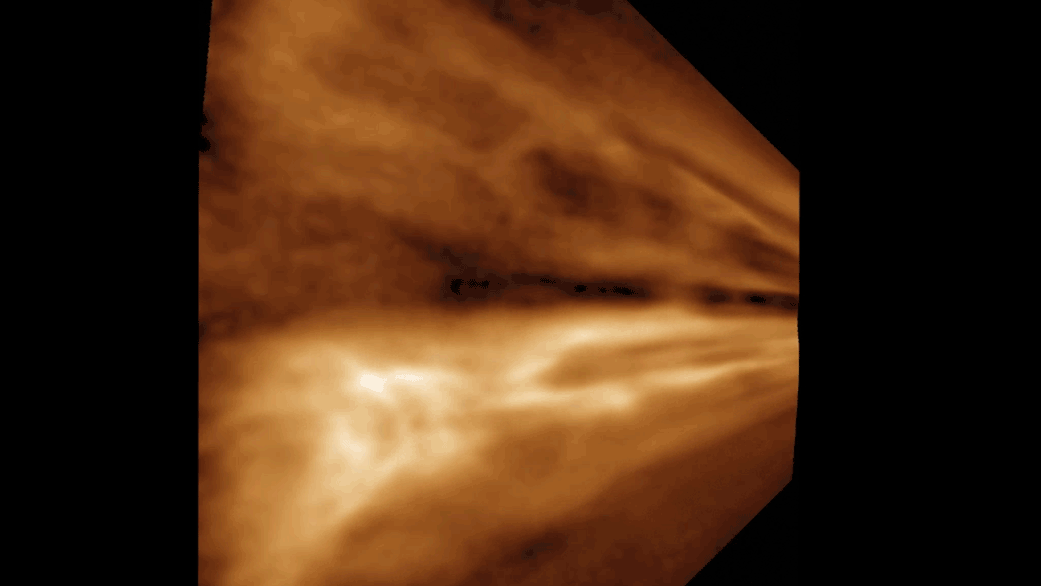
NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover used one of its navigation cameras to take a series of images of drifting clouds just before sunrise on March 18, 2023, the 738th Martian day, or sol, of the mission.
Scientists on both the Perseverance mission and NASA's Curiosity rover mission are studying the formation process of Martian clouds.
A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust).
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover.
For more about Perseverance:
mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/