Curiosity’s Quadrant Themes
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/USGS-Flagstaff/University of Arizona |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
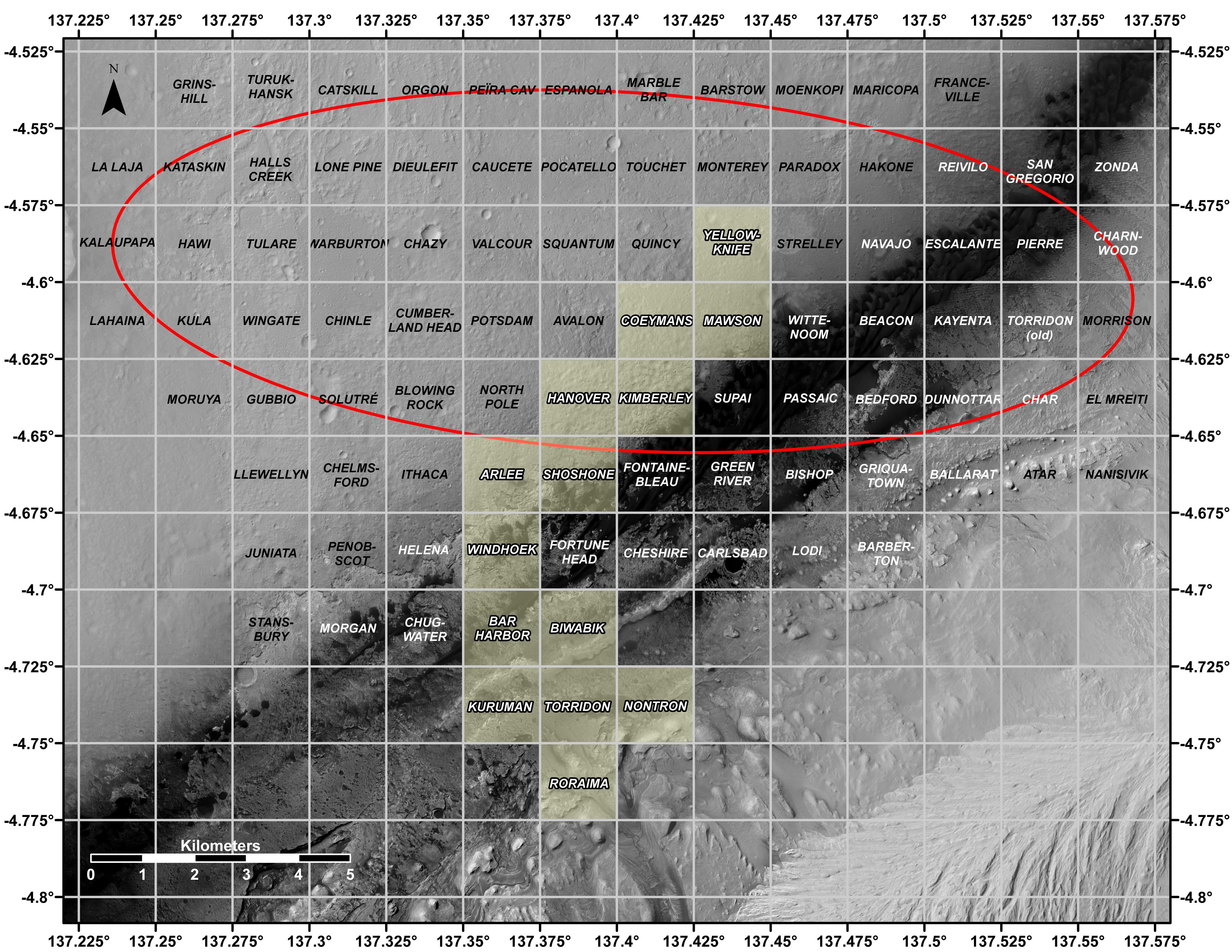
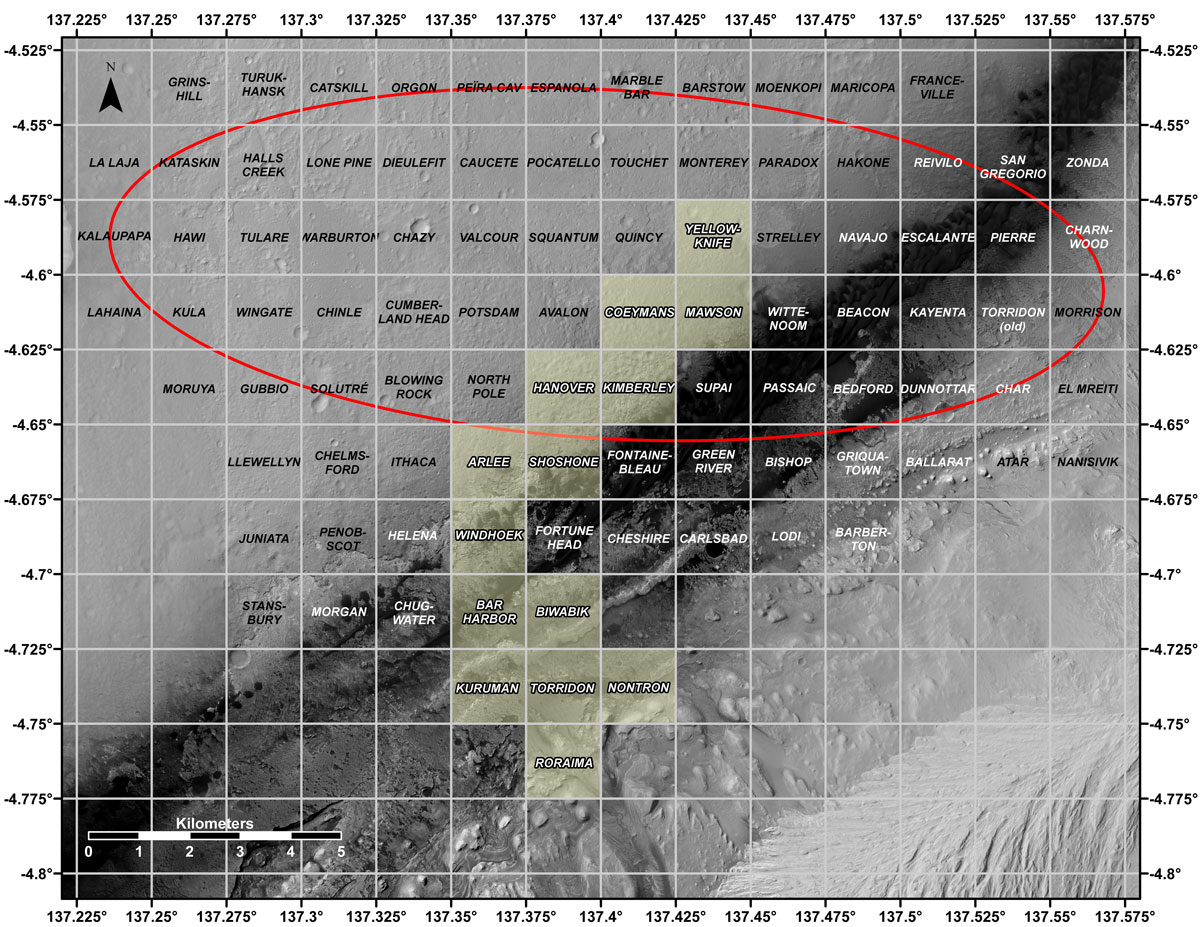
This map shows all the quadrant themes for NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover, which is currently in the Roraima quadrant seen at the bottom. The red oval indicates the landing ellipse where the rover was targeted to touch down in 2012. The yellow-tinted quadrants are areas the rover has driven through since then. Themes are chosen in advance of the rover’s arrival in a new quadrant; the rover’s path couldn’t be planned until after the team knew where it landed. Martian latitude and longitude is provided around the outside of the map.
With the Curiosity mission, scientists began using quadrant themes to organize the long lists of unofficial nicknames needed to catalog its observations, whether hills, craters, boulders, rocks, and even tiny features on rock surfaces. Scientist deplete these lists of names quickly – especially with Curiosity, which has used more than 10,000 names over nearly 11 years of exploring Mars. Different science “targets” all require names – including targets for the rover’s cameras, the rocks on which it places its arm instruments and drill, and the surfaces it zaps with its laser instrument.
Curiosity’s team chooses quadrant themes based on sites of geological interest on Earth. Its current quadrant, Roraima, is named for the northernmost state of Brazil, and for Mount Roraima, the highest peak in the Pacaraima mountains, located near the border of Venezuela, Brazil, and Guyana. The sulfate-enriched region Curiosity is currently exploring, with its flat-topped hills and steep slopes, reminded the rover team of the “table-top” mountains in the Pacaraima range. This is the first quadrant theme the team has chosen related to South America.
Previously explored quadrants include Torridon, based on sites in Scotland, and Nontron, based on the French region where the town of Nontron can be found. While in the Nontron quadrant, which was located in a clay-enriched region, Curiosity drilled a rock sample that included a notable amount of nontronite – a clay mineral that was first discovered on Earth near Nontron.
Each quadrant is 0.025 degrees of latitude and longitude, or approximately 0.7 miles (1.2 kilometers) on each side.
Curiosity was built by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed by Caltech in Pasadena, California. JPL leads the mission on behalf of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
For more about Curiosity, visit:
http://mars.nasa.gov/msl