Images
Boron, Sodium and Chlorine in Mineral Vein 'Diyogha'

December 13, 2016
Examination of a calcium sulfate vein called "Diyogha" by the Chemical and Camera (ChemCam) instrument on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover found boron, sodium and chlorine.
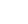
At left, an image from Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam) shows the context of the pale vein in mudstone of the Murray Formation on lower Mount Sharp. A red outline marks the area included in a magnified view, at right, from ChemCam's remote micro-imager. The magnified view is annotated with indicators of boron, sodium and chlorine content detected by ChemCam at individual points hit with the instrument's laser.
Targets such as Diyogha indicate that the calcium sulfate veins in the Murray bedrock may have a source that is rich in evaporite minerals. Boron, chlorine and sodium all can be present in evaporites. Diyogha was examined on Sept. 7, 2016, during the 1,454th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars.
The scale bar for the inset is 10.4 millimeters, or about 0.41 inch. The ChemCam image is enhanced with color information from Mastcam. The vein is whiter in the middle due to the dust being blown away by impact of the laser. Point 2 hits a pebble and not the sulfate vein, so its chemistry is not included on the figure.
Mastcam and ChemCam are two of 10 instruments in Curiosity's science payload. Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego, developed and operates Mastcam. The U.S. Department of Energy's Los Alamos National Laboratory, in Los Alamos, New Mexico, developed ChemCam in partnership with scientists and engineers funded by the French national space agency (CNES), the University of Toulouse and the French national research agency (CNRS).