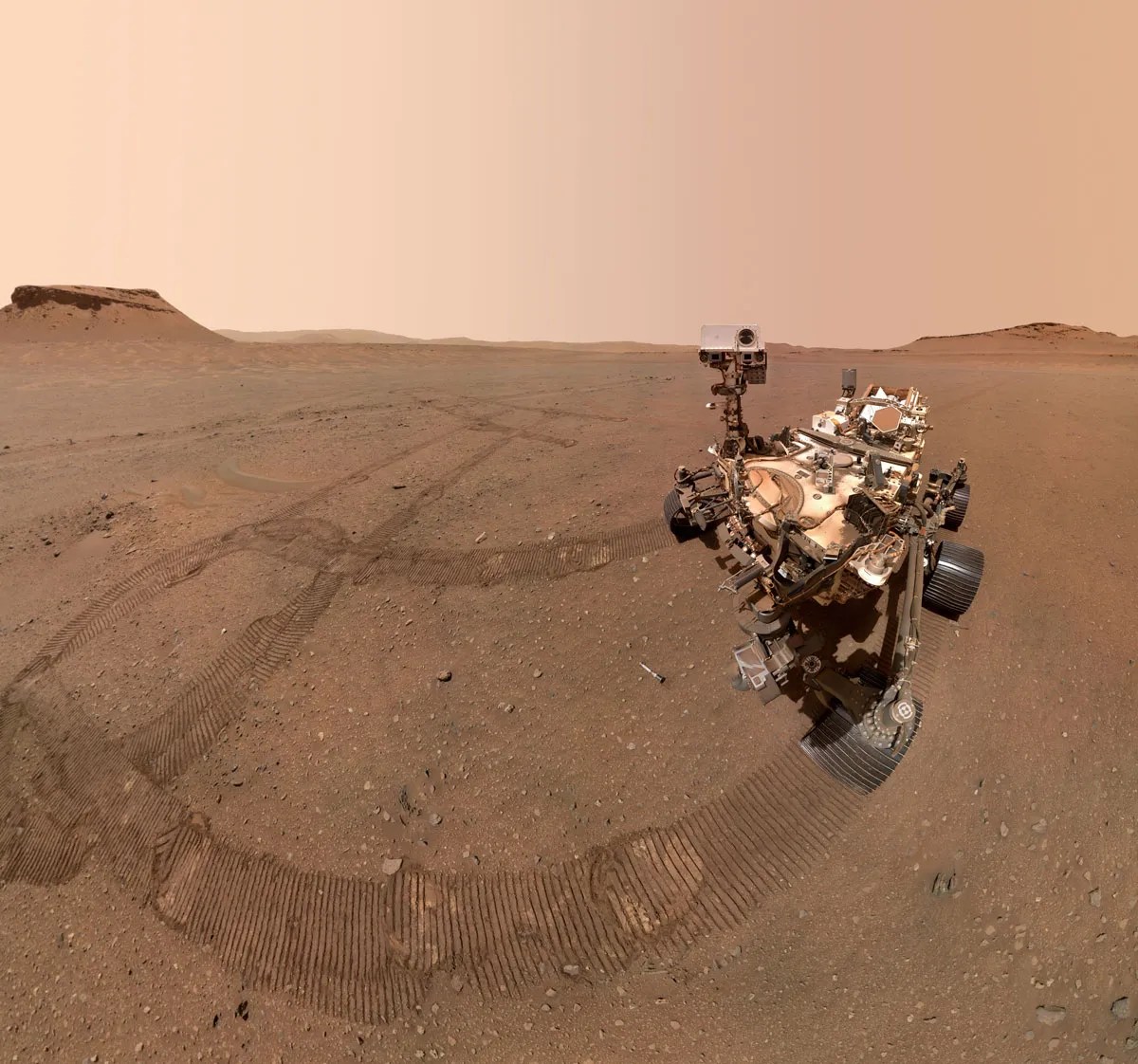
2 min read
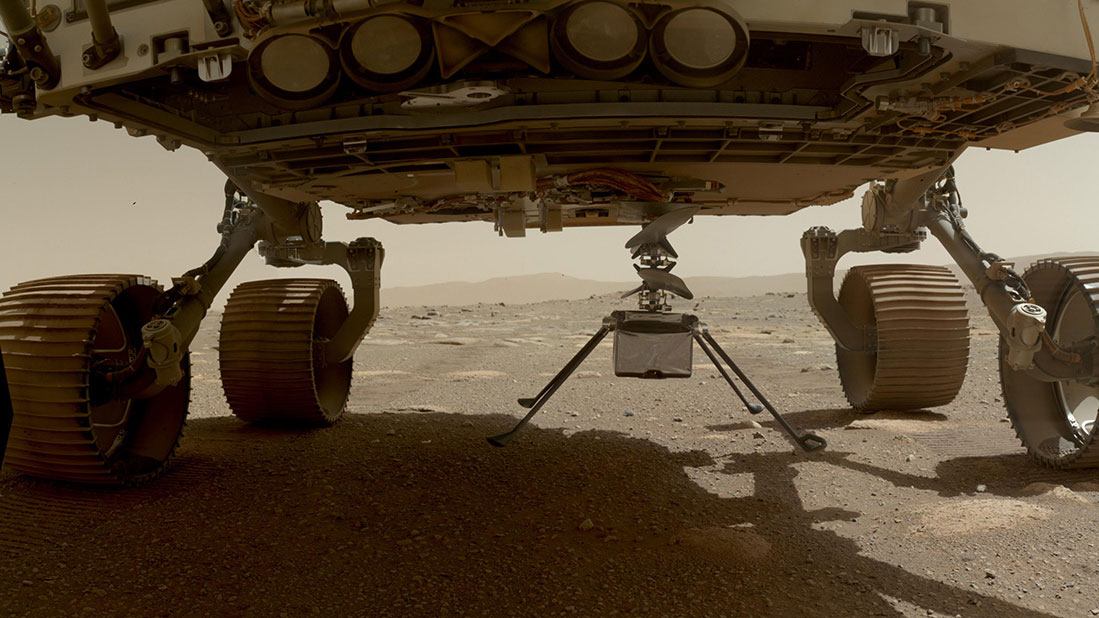

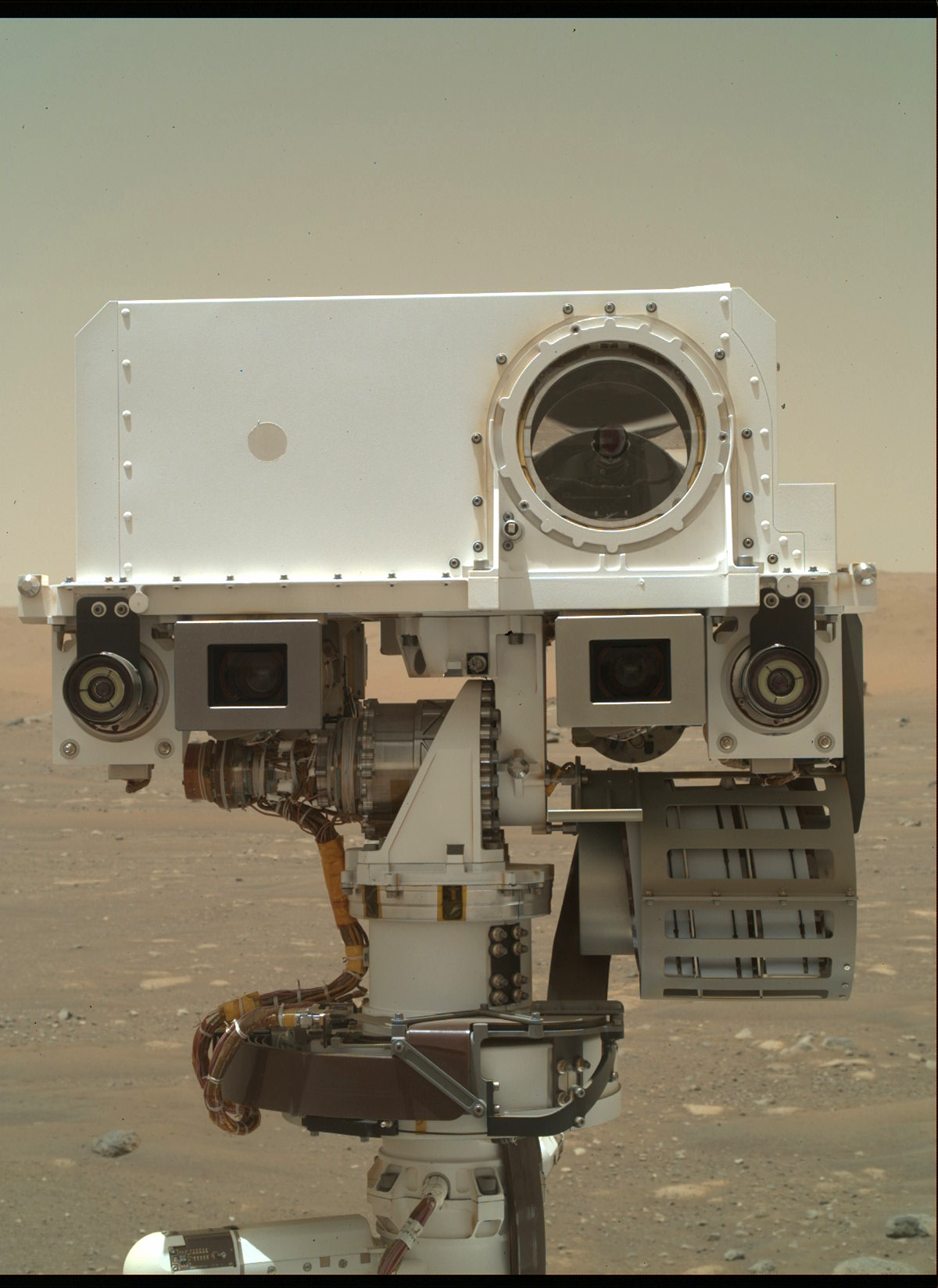
Within a few days, Ingenuity will be on the surface of Mars. Until now it has been connected to the Perseverance rover, which allowed Ingenuity to charge its battery as well as use a thermostat-controlled heater powered by the rover. This heater keeps the interior at about 45 degrees F through the bitter cold of the Martian night, where temperatures can drop to as low as -130F. That comfortably protects key components such as the battery and some of the sensitive electronics from harm at very cold temperatures.
Before Ingenuity drops the last few inches onto its airfield, Perseverance will charge up the little helicopter's battery to a 100 percent state-of-charge. That's a good thing, because Ingenuity has to run its own heater from its own battery after the drop. No more free power from the rover!
But there is another free source of energy on Mars: the Sun! The Sun's energy is weaker at Mars-a little over half of what we would find here on Earth on a bright, sunny day. But it's enough for Ingenuity's high-tech solar panel to charge the battery. Of course, this means that the rover will drive away from Ingenuity after the drop so that we uncover the solar panel. This will occur as soon as possible after the drop.
Ingenuity can't afford to keep the temperature of its interior at a "balmy" 45F -that takes too much precious energy from the battery. Instead, when it wakes up on the surface after being dropped, it sets its thermostat to about 5F or lower. Then it's off to survive the first night on its own!
The Ingenuity team will be anxiously waiting to hear from the helicopter the next day. Did it make it through the night? Is the solar panel working as expected? The team will check the temperatures and the battery recharge performance over the next couple of days. If it all looks good, then it's onto the next steps: unlocking the rotor blades, and testing out all the motors and sensors.
Written by Bob Balaram, Chief Engineer for the Mars Helicopter Project at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory